Pleomorphic adenoma of the lip: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 40376544
- PMCID: PMC12078932
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjaf311
Pleomorphic adenoma of the lip: a case report and literature review
Abstract
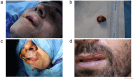
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) most commonly affects the major salivary glands but can also involve the minor salivary glands, particularly those of the hard and soft palate. However, the current study aims to present a case of upper lip PA. A 29-year-old male presented with a painless, firm, slow-growing swelling (1.5 × 1.5 cm) on the left upper lip. Ultrasonography showed a solid, hypoechoic nodule with irregular margins and mild peripheral vascularity. The encapsulated tumor was excised, and histopathology confirmed PA. At the 7-month follow-up, no evidence of recurrence was observed. Though typically seen in adults aged 40-70, PA can affect younger patients. Complete excision with clear margins is essential due to the risk of recurrence or malignant transformation. PA should be considered in the differential diagnosis of upper lip swellings.
Keywords: benign mixed tumor; lip tumor; neoplasm; salivary gland.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. © The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pleomorphic adenoma of the upper lip: A rare case report.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2020 Jul-Dec;11(2):289-291. doi: 10.4103/njms.NJMS_20_17. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2020. PMID: 33897197 Free PMC article.
-
Pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor) of the upper lip: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jun 16;12(17):3138-3143. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3138. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38898865 Free PMC article.
-
RECURRENT PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA OF THE UPPER LIP: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE.Niger J Med. 2015 Jul-Sep;24(3):277-80. Niger J Med. 2015. PMID: 27487602 Review.
-
An unusual exophytic pleomorphic adenoma on the upper lip skin without mucosa involvement: a case report.Arch Craniofac Surg. 2024 Aug;25(4):201-204. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2023.00626. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39020470 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary gland tumour of the lip: report of two cases and literature review.Cent Afr J Med. 2009 May-Aug;55(5-8):43-6. Cent Afr J Med. 2009. PMID: 21977828 Review.
References
-
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Ali SM, et al. Giant pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland extending to the parapharyngeal space: a rare case report. Int J Case Rep Images 2018;9:100914Z01AS2018. 10.5348/100914Z01AS2018CR - DOI
-
- Alrehaili J. A unique pleomorphic adenoma in the minor salivary glands of the upper lip: a case report. Pathol Lab Med Int 2023;15:37–41. 10.2147/PLMI.S415283 - DOI
-
- Abdullah AS, Ahmed AG, Mohammed SN, et al. Benign tumor publication in one year (2022): a cross-sectional study. Barw Med J 2023;1:20–5.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

