Opportunities and challenges of lifestyle intervention-based digital therapeutics in LDL-C management: a scoping review
- PMID: 40376548
- PMCID: PMC12078976
- DOI: 10.1177/20406223251334439
Opportunities and challenges of lifestyle intervention-based digital therapeutics in LDL-C management: a scoping review
Abstract
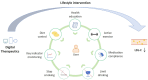
Background: In recent decades, the prevalence of dyslipidemia, especially high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), has risen sharply in China. Although lifestyle interventions are important, traditional face-to-face approaches have limitations. Digital Therapeutics (DTx) can provide an effective solution by delivering remote medical interventions to patients via software and hardware, thereby optimizing existing clinical treatment methods with enhanced convenience and accessibility.
Objectives: This study aims to explore the current evidence on the effect of lifestyle intervention-based Digital Therapeutics (LI-DTx) on high LDL-C, and to analyze their advantages and disadvantages.
Eligibility criteria: This scoping review examines clinical studies assessing the effects of DTx on LDL-C levels. Papers were included in the final analysis if there was evidence that DTx had effects on lowering LDL-C levels.
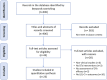
Sources of evidence: Papers that were published between January 2014 and December 2023 were included in the PubMed database.
Charting methods: Data extracted from the publications included country, year, study type, study population, sample size, study duration, intervention, and changes in LDL-C level.
Results: A total of 23 target literature were identified. Twenty-one studies confirmed that LI-DTx could optimize the LDL-C level through remote lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, medication, and health education, of which 14 studies reported a significant reduction in LDL-C level (p < 0.05). In the future, the development and design of DTx will need to improve intelligence, personalization, applicability, real-time performance, and data security; integrate with traditional healthcare systems; facilitate multidisciplinary collaboration in dyslipidemia management; and enhance long-term patient engagement with DTx platforms.
Conclusion: LI-DTx may offer a more effective and sustainable solution for LDL-C management, although several challenges remain. Further randomized controlled clinical trials are needed to provide scientific support for its efficacy and safety.
Keywords: LDL-C; applications; cognitive behavior therapy; digital therapeutics; lifestyle modification.
© The Author(s), 2025.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipid Screening in Childhood for Detection of Multifactorial Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Aug. Report No.: 14-05204-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Aug. Report No.: 14-05204-EF-1. PMID: 27559550 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Digital therapeutics in hypertension: How to make sustainable lifestyle changes.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024 Oct;26(10):1125-1132. doi: 10.1111/jch.14894. Epub 2024 Sep 9. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024. PMID: 39248244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benchmarking the clinical outcomes of Healthentia SaMD in chronic disease management: a systematic literature review comparison.Front Public Health. 2024 Dec 24;12:1488687. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1488687. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39776481 Free PMC article.
-
Effects on Adherence to a Mobile App-Based Self-management Digital Therapeutics Among Patients With Coronary Heart Disease: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 Feb 15;10(2):e32251. doi: 10.2196/32251. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022. PMID: 34906924 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
Cited by
-
Effects of 12 nutritional interventions on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomized trials.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025 Aug 7;22(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12986-025-00968-3. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40775771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China 2021: an updated summary. Biomed Environ Sci 2022; 35(7): 573–603. - PubMed
-
- Joint Committee on the Chinese Guidelines for Lipid Management. Chinese guidelines for lipid management (2023). Chin J Cardiol 2023; 51(3): 221–255. - PubMed
-
- European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation, Reiner Z, Catapano AL, et al.. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur Heart J 2011; 32(14): 1769–1818. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials