A cross-sectional study evaluating insulin injection techniques and the impact of instructions from various healthcare professionals on insulin users in the southern region of Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 40376558
- PMCID: PMC12080473
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19394
A cross-sectional study evaluating insulin injection techniques and the impact of instructions from various healthcare professionals on insulin users in the southern region of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: It is evident that proper use of the insulin injection technique (IIT) is important for optimizing the efficacy of the therapy. Despite the readily available manufacturers' instructions, healthcare professionals (HCPs) play a major role in educating patients. This study aims to investigate the knowledge, practices, and challenges faced by insulin users regarding IIT, as well as the impact of healthcare professionals' education on it.
Methods: We conducted a questionnaire-based cross-sectional study using a validated online questionnaire to gather demographic and clinical data, as well as the participants' knowledge, practices, and challenges related to insulin therapy.
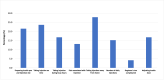
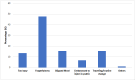
Results: The mean age of the participants was 38.25 ± 15.58 (mean ± SD) years, with a nearly equal distribution of genders. Thirty-six percent of the participants educated by the diabetes educators demonstrated an appropriate IIT, such as storage, priming the insulin pen (54%), skin folding (63%), injection hold time, and "use-by" date. Furthermore, the absence of diabetes education specialist training increases the likelihood of errors, potentially leading to a loss of glycemic control. Patients reported carrying insulin when traveling as one of the major challenges (27.9%), followed by timely injections (23.7%), priming (21.6%), and adjusting the insulin dose (16.8%). Forgetfulness (47.7%), traveling or altering the regular routine (15.5%), missing a meal (15.5%), and being overly busy (13.5%) were among the reasons for missing the insulin dose; all of which are easily manageable with proper education.
Conclusion: Consistent education and re-education are necessary for the insulin users to resolve the issues associated with suboptimal IIT. The inclusion of all stakeholders in insulin therapy, particularly the diabetes education specialists, is essential. Therefore, the Ministry of Health in Saudi Arabia should take the initiative to ensure that appropriately trained diabetes education specialists, pharmacists, nurses and other HCPs assess and follow up on patients.
Keywords: Barriers; Diabetes education; Diabetes mellitus; Healthcare professionals; Insulin injection technique.
©2025 Shaik Alavudeen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Competency of Prefilled Insulin Pen Usage Among Diabetes Patients in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-sectional Study.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(3):240-246. doi: 10.2174/1573399814666180528081552. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019. PMID: 29804535
-
Healthcare professional and patient assessment of a new prefilled insulin pen versus two widely available prefilled insulin pens for ease of use, teaching and learning.Curr Med Res Opin. 2012 Jan;28(1):3-13. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2011.644427. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012. PMID: 22114905 Clinical Trial.
-
Administration technique and storage of disposable insulin pens reported by patients with diabetes.Diabetes Educ. 2012 Sep-Oct;38(5):651-8. doi: 10.1177/0145721712450921. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Diabetes Educ. 2012. PMID: 22722612
-
Advance Insulin Injection Technique and Education With FITTER Forward Expert Recommendations.Mayo Clin Proc. 2025 Apr;100(4):682-699. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2025.01.004. Mayo Clin Proc. 2025. PMID: 40180487 Review.
-
Worldwide Injection Technique Questionnaire Study: Injecting Complications and the Role of the Professional.Mayo Clin Proc. 2016 Sep;91(9):1224-30. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.06.012. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016. PMID: 27594186 Review.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Osman MT, Jaffar A, Rashed MR, Hassan MR, Supian ZA. Education of correct insulin injection technique amongst diabetic patients: outcome study from Malaysia. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences. 2016;5:198–205.
-
- Alavudeen SS, Khobrani M, Dhanapal CK, Mir JI, Alshahrani SM, Khan NA, Alhossan A. Comparative evaluation of biphasic insulin with metformin and triple oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA) in type 2 diabetes patients. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2020;28:210–214. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.11.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alhagawy AJ, Yafei S, Hummadi A, Abutaleb R, Hakamy M, Alzughbi T, Gharawi N, Moafa M, Mokali A, Alhiqwy I, Altherwi M. Barriers and attitudes of primary healthcare physicians to insulin initiation and intensification in Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022;19:16794. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416794. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical