Nanobiosensors in neurodegenerative disease diagnosis: A promising pathway for early detection
- PMID: 40376568
- PMCID: PMC12078979
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076251342457
Nanobiosensors in neurodegenerative disease diagnosis: A promising pathway for early detection
Abstract
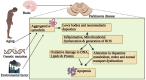
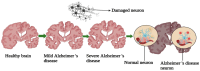
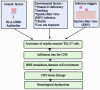
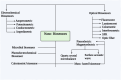
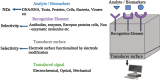
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, are characterized by progressive neuronal loss, leading to cognitive and motor impairments. Early diagnosis remains a challenge due to the slow progression of symptoms and the limitations of current diagnostic methods. Nanobiosensors, leveraging the high sensitivity and specificity of nanotechnology, offer a promising, noninvasive, and cost-effective approach for detecting disease biomarkers at ultra-low concentrations. This review highlights recent advancements in nanobiosensor technology, including the integration of gold nanoparticles, quantum dots, and carbon nanotubes, which have significantly enhanced biomarker detection precision. Furthermore, it examines the advantages of nanobiosensors over traditional diagnostic techniques, such as improved sensitivity, rapid detection, and minimal invasiveness. The potential of these innovative sensors to revolutionize early disease detection and improve patient outcomes is discussed, along with existing challenges in clinical translation, including stability, reproducibility, and regulatory considerations. Addressing these limitations will be crucial for integrating nanobiosensors into routine clinical practice and advancing personalized medicine for neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Neurodegenerative diseases; Parkinson's disease; biomarkers; biosensing; electrochemical sensors; nanobiosensors; nanotechnology.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Lamptey RNL, Chaulagain B, Trivedi R, et al. A review of the common neurodegenerative disorders: current therapeutic approaches and the potential role of nanotherapeutics. Int J Mol Sci [Internet] 2022. [cited 2024 Dec 1]; 23: 1851. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/3/1851 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty S. Study of Neurodegenerative Disease Progression and Early Detection using Deep Learning Algorithms . Graduate School, Inje University, 2020.
-
- Porsteinsson AP, Isaacson RS, Knox S, et al. Diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease: clinical practice in 2021. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2021; 8: 371–386. - PubMed
-
- Deuschl G, Beghi E, Fazekas F, et al. The burden of neurological diseases in Europe: an analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Public Health [Internet] 2020. [cited 2024 Dec 1]; 5: e551–e567. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2468266720301900 - PubMed
-
- Choi HK, Choi J-H, Yoon J. An updated review on electrochemical nanobiosensors for neurotransmitter detection. Biosensors [Internet] 2023. [cited 2024 Dec 1]; 13: 892. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6374/13/9/892 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

