The application of ultrasound artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of endometrial diseases: Current practice and future development
- PMID: 40376569
- PMCID: PMC12078975
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076241310060
The application of ultrasound artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of endometrial diseases: Current practice and future development
Abstract
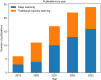
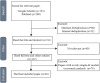
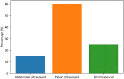
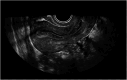
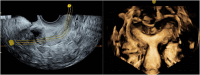
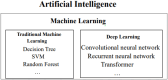
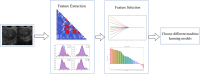
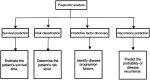
Diagnosis and treatment of endometrial diseases are crucial for women's health. Over the past decade, ultrasound has emerged as a non-invasive, safe, and cost-effective imaging tool, significantly contributing to endometrial disease diagnosis and generating extensive datasets. The introduction of artificial intelligence has enabled the application of machine learning and deep learning to extract valuable information from these datasets, enhancing ultrasound diagnostic capabilities. This paper reviews the progress of artificial intelligence in ultrasound image analysis for endometrial diseases, focusing on applications in diagnosis, decision support, and prognosis analysis. We also summarize current research challenges and propose potential solutions and future directions to advance ultrasound artificial intelligence technology in endometrial disease diagnosis, ultimately improving women's health through digital tools.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; deep learning; disease diagnosis; endometrium; ultrasound images.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Unuane D, Tournaye H, Velkeniers B, et al. Endocrine disorders & female infertility. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 25: 861–873. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri RL. Female infertility. In: Yen and Jaffe’s reproductive endocrinology. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019, pp. 556–581.e7.
-
- Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Ferrero S, Mangili G, et al. A systematic review on endometriosis during pregnancy: diagnosis, misdiagnosis, complications and outcomes. Hum Reprod Update 2015; 22: 70–103. - PubMed
-
- Vieira MDC, Vitagliano A, Rossette MC, et al. Endometrial polyps: update overview on etiology, diagnosis, natural history and treatment. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2022; 49: 22–27.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

