YOLOv8 framework for COVID-19 and pneumonia detection using synthetic image augmentation
- PMID: 40376574
- PMCID: PMC12078974
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076251341092
YOLOv8 framework for COVID-19 and pneumonia detection using synthetic image augmentation
Abstract
Objective: Early and accurate detection of COVID-19 and pneumonia through medical imaging is critical for effective patient management. This study aims to develop a robust framework that integrates synthetic image augmentation with advanced deep learning (DL) models to address dataset imbalance, improve diagnostic accuracy, and enhance trust in artificial intelligence (AI)-driven diagnoses through Explainable AI (XAI) techniques.
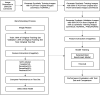
Methods: The proposed framework benchmarks state-of-the-art models (InceptionV3, DenseNet, ResNet) for initial performance evaluation. Synthetic images are generated using Feature Interpolation through Linear Mapping and principal component analysis to enrich dataset diversity and balance class distribution. YOLOv8 and InceptionV3 models, fine-tuned via transfer learning, are trained on the augmented dataset. Grad-CAM is used for model explainability, while large language models (LLMs) support visualization analysis to enhance interpretability.
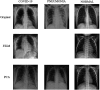
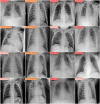
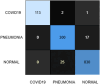
Results: YOLOv8 achieved superior performance with 97% accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, outperforming benchmark models. Synthetic data generation effectively reduced class imbalance and improved recall for underrepresented classes. Comparative analysis demonstrated significant advancements over existing methodologies. XAI visualizations (Grad-CAM heatmaps) highlighted anatomically plausible focus areas aligned with clinical markers of COVID-19 and pneumonia, thereby validating the model's decision-making process.
Conclusion: The integration of synthetic data generation, advanced DL, and XAI significantly enhances the detection of COVID-19 and pneumonia while fostering trust in AI systems. YOLOv8's high accuracy, coupled with interpretable Grad-CAM visualizations and LLM-driven analysis, promotes transparency crucial for clinical adoption. Future research will focus on developing a clinically viable, human-in-the-loop diagnostic workflow, further optimizing performance through the integration of transformer-based language models to improve interpretability and decision-making.
Keywords: COVID-19 detection; YOLOv8; medical image analysis; pneumonia classification; synthetic image augmentation.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ResViT FusionNet Model: An explainable AI-driven approach for automated grading of diabetic retinopathy in retinal images.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Mar;186:109656. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109656. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39823821
-
Revolutionizing breast ultrasound diagnostics with EfficientNet-B7 and Explainable AI.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01404-3. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39223507 Free PMC article.
-
An Explainable AI Paradigm for Alzheimer's Diagnosis Using Deep Transfer Learning.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;14(3):345. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030345. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337861 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Cardiovascular Imaging-A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 31;15(11):1399. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111399. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilizing large language models for gastroenterology research: a conceptual framework.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 1;18:17562848251328577. doi: 10.1177/17562848251328577. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40171241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mayo Clinic. Pneumonia - symptoms and causes. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pneumonia/symptoms-causes... (accessed 25 November 2024).
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Pneumonia. Available at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/pneumonia (accessed 25 November 2024).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Pneumonia. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/pneumonia/index.html (accessed 25 November 2024).
-
- Cleveland Clinic. Pneumonia: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4471-pneumonia (accessed 25 November 2024).
-
- American Lung Association. Pneumonia symptoms and diagnosis. Available at: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/... (accessed 25 November 2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

