Cancer-on-a-chip for precision cancer medicine
- PMID: 40376718
- PMCID: PMC12082394
- DOI: 10.1039/d4lc01043d
Cancer-on-a-chip for precision cancer medicine
Abstract
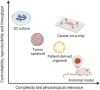
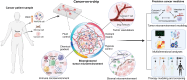
Many cancer therapies fail in clinical trials despite showing potent efficacy in preclinical studies. One of the key reasons is the adopted preclinical models cannot recapitulate the complex tumor microenvironment (TME) and reflect the heterogeneity and patient specificity in human cancer. Cancer-on-a-chip (CoC) microphysiological systems can closely mimic the complex anatomical features and microenvironment interactions in an actual tumor, enabling more accurate disease modeling and therapy testing. This review article concisely summarizes and highlights the state-of-the-art progresses in CoC development for modeling critical TME compartments including the tumor vasculature, stromal and immune niche, as well as its applications in therapying screening. Current dilemma in cancer therapy development demonstrates that future preclinical models should reflect patient specific pathophysiology and heterogeneity with high accuracy and enable high-throughput screening for anticancer drug discovery and development. Therefore, CoC should be evolved as well. We explore future directions and discuss the pathway to develop the next generation of CoC models for precision cancer medicine, such as patient-derived chip, organoids-on-a-chip, and multi-organs-on-a-chip with high fidelity. We also discuss how the integration of sensors and microenvironmental control modules can provide a more comprehensive investigation of disease mechanisms and therapies. Next, we outline the roadmap of future standardization and translation of CoC technology toward real-world applications in pharmaceutical development and clinical settings for precision cancer medicine and the practical challenges and ethical concerns. Finally, we overview how applying advanced artificial intelligence tools and computational models could exploit CoC-derived data and augment the analytical ability of CoC.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

