Zinc in psychosis (Review)
- PMID: 40376988
- PMCID: PMC12105465
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13566
Zinc in psychosis (Review)
Abstract
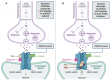
Zinc (Zn) may be associated with schizophrenia (SCH), since its altered homeostasis can contribute to abnormal glutamatergic neurotransmission, inflammation, neurodegeneration and autoimmune abnormalities. It has been proposed that a number of patients with SCH could benefit from the use of Zn, either on its own or along with vitamins C, E and B6, and prenatal supplementation of Zn during the gestation period can mitigate the lipopolysaccharide‑induced rat model of maternal immune activation. The aim of the present review was to summarize the various effects of Zn dyshomeostasis on patients with psychosis and to clarify in what ways they could benefit from Zn supplementation.
Keywords: psychosis; schizophrenia; zinc; zinc homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
DAS is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Membrane lipids in schizophrenia and early phases of psychosis: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets?].Encephale. 2020 Jun;46(3):209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2019.11.009. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Encephale. 2020. PMID: 32151446 French.
-
Neural basis of psychosis-related behaviour in the infection model of schizophrenia.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Dec 7;204(2):322-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.12.022. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19154759
-
[Effects of supplementing of calcium, iron and zinc on women's health during pregnancy].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001 Nov;35(6):365-9. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001. PMID: 11840760 Chinese.
-
[Stress and psychotic transition: A literature review].Encephale. 2016 Aug;42(4):367-73. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2015.10.001. Epub 2016 May 6. Encephale. 2016. PMID: 27161263 Review. French.
-
[Cholinergic hypothesis in psychosis following traumatic brain injury and cholinergic hypothesis in schizophrenia: a link?].Encephale. 2007 Sep;33(4 Pt 1):616-20. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(07)92062-x. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18033152 Review. French.
References
-
- Pfeiffer CC, Iliev V. A study of Zn deficiency and copper excess in the schizophrenias. In: Pfeiffer CC, editor. Neurobiology of Trace Metals Zinc and Copper. Academic Press; New York: 1972. pp. 141–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

