Translation elongation: measurements and applications
- PMID: 40377059
- PMCID: PMC12087489
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2504727
Translation elongation: measurements and applications
Abstract
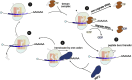
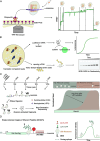
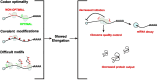
Translation converts genetic information in mRNAs into functional proteins. This process occurs in four major steps: initiation, elongation, termination and ribosome recycling; each of which profoundly impacts mRNA stability and protein yield. Over recent decades, regulatory mechanisms governing these aspects of translation have been identified. In this review, we focus on the elongation phase, reviewing the experimental methods used to measure elongation rates and discussing how the measurements shed light on the factors that regulate elongation and ultimately gene expression.
Keywords: RNA modification; Translation elongation; codon optimality; ribosome; ribosome profiling; single molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical modifications to mRNA nucleobases impact translation elongation and termination.Biophys Chem. 2022 Jun;285:106780. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2022.106780. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Biophys Chem. 2022. PMID: 35313212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translation elongation inhibitors stabilize select short-lived transcripts.RNA. 2024 Nov 18;30(12):1572-1585. doi: 10.1261/rna.080138.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39293933 Free PMC article.
-
Codon usage regulates protein structure and function by affecting translation elongation speed in Drosophila cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Aug 21;45(14):8484-8492. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx501. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28582582 Free PMC article.
-
High-Resolution Ribosome Profiling for Determining Ribosome Functional States During Translation Elongation.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2428:173-186. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1975-9_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35171480
-
The ribosome in action: Tuning of translational efficiency and protein folding.Protein Sci. 2016 Aug;25(8):1390-406. doi: 10.1002/pro.2950. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27198711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
