During recombinase-mediated homology recognition RecQ helicases inhibit formation of toxic long-lived D-loops that could promote genomic instability
- PMID: 40377216
- PMCID: PMC12082448
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf426
During recombinase-mediated homology recognition RecQ helicases inhibit formation of toxic long-lived D-loops that could promote genomic instability
Abstract
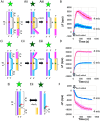
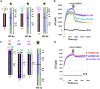
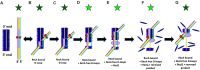
Mutations in RecQ family helicases underlie human genetic disorders associated with genomic instability and cancer predisposition, but questions remain about how properly functioning RecQ reduces these deleterious effects. Importantly, some of the deleterious effects may result from incorrect repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by recombinase proteins. Displacement loops (D-loops) are three-strand intermediates formed by recombinases during repair of DSB. RecQ helicases might enhance genome stability by disassembling incorrect recombinase-mediated D-loops formed between mismatched sequences and/or between short regions of accidental homology. We used bulk FRET and gel electrophoresis assays to probe the effects of RecQ family helicases in the context of ongoing recombinase-mediated D-loop formation. We found that RecQ does not differentially promote disassembly of short D-loops or D-loops that include mismatched base pairs. Thus, RecQ does not reduce genomic instability by discriminating against incorrect D-loops. In contrast, our results suggest that RecQ intervenes during D-loop formation to limit the length of recombinase-mediated D-loops. Without that intervention, D-loops can become so long that they do not spontaneously reverse. We suggest that RecQ prevents undesirable long-lived connections between chromosomes that could compromise chromosome metabolism and/or segregation and promote genomic instability.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The RecQ DNA helicases in DNA repair.Annu Rev Genet. 2010;44:393-417. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163602. Annu Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 21047263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RecQ helicases in DNA double strand break repair and telomere maintenance.Mutat Res. 2012 Aug 1;736(1-2):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 21689668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RECQ-like helicases Sgs1 and BLM regulate R-loop-associated genome instability.J Cell Biol. 2017 Dec 4;216(12):3991-4005. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201703168. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 29042409 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of RecQ helicases in pathways of DNA metabolism and maintenance of genomic stability.Biochem J. 2006 Sep 15;398(3):319-37. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060450. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16925525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobile D-loops are a preferred substrate for the Bloom's syndrome helicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 2;34(8):2269-79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl258. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16670433 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

