A specialized TFIIB is required for transcription of transposon-targeting noncoding RNAs
- PMID: 40377217
- PMCID: PMC12082453
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf427
A specialized TFIIB is required for transcription of transposon-targeting noncoding RNAs
Abstract
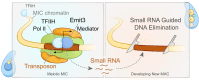
Transposable elements (TEs) pose threats to genome stability. Therefore, small RNA-mediated heterochromatinization suppresses the transcription and hence the mobility of TEs. Paradoxically, transcription of noncoding RNA (ncRNA) from TEs is needed for the production of TE-targeting small RNAs and/or recruiting the silencing machinery to TEs. Hence, specialized RNA polymerase II (Pol II) regulators are required for such unconventional transcription in different organisms, including the developmental stage-specific Mediator complex (Med)-associated proteins in the ncRNA transcription from TE-related sequences in Tetrahymena. Yet it remains unclear how the Pol II transcriptional machinery is assembled at TE-related sequences for the ncRNA transcription. Here, we report that Pol II is regulated by Emit3, a stage-specific TFIIB-like protein specialized in TE transcription. Emit3 interacts with the TFIIH complex and localizes to TE-dense regions, especially at sites enriched with a G-rich sequence motif. Deletion of Emit3 globally abolishes Pol II-chromatin association in the meiotic nucleus, disrupts the chromatin binding of Med, and impairs the TE-biased localization of TFIIH. Conversely, Emit3's preferential localization to TE-rich loci relies in part on Med-associated proteins. These findings suggest that Emit3, TFIIH, and Med-associated proteins work together to initiate Pol II ncRNA transcription from TE-dense regions, possibly in a sequence-dependent manner.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

