Dynamics of HBV biomarkers during nucleos(t)ide analog treatment: A 14-year study
- PMID: 40377494
- PMCID: PMC12088637
- DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000708
Dynamics of HBV biomarkers during nucleos(t)ide analog treatment: A 14-year study
Abstract
Background: Circulating HBsAg, HBV RNA, and hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) are potential biomarkers for the response to nucleos(t)ide analog (NA) treatment discontinuation in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We retrospectively investigated the long-term kinetics of HBsAg, HBV RNA, and HBcrAg in HBeAg-negative patients treated with NA for up to 14 years in a prospective cohort study.
Methods: Ninety-six patients (mean age 65 y, 77% male, 52% with cirrhosis, all HBV genotype D) who were undergoing first (n=33, group A) or second-line (n=63, group B) treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate were included. HBV biomarkers collected during tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment were measured in 384 serum samples stored at -20 °C. The combined biomarker endpoints associated with functional cure following NA discontinuation included HBsAg <1000 IU/mL, HBV RNA <54 copies/mL, and HBcrAg <2 log U/mL.
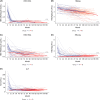
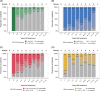
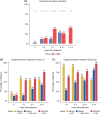
Results: Before NA treatment, HBV RNA and HBcrAg were detectable in 85% (mean 3.9±2.3 [range, 0-9.2] log10 copies/mL) and 80% (mean 4.3±1.9 [2-8.9] log10 U/mL), respectively, of the patients in group A. In groups A and B, the percentages of patients with detectable HBV RNA levels decreased to 53% and 34%, respectively, during years 8-10 of NA treatment, and to 29% in group B during years 11-14 to 29%. HBcrAg could be quantified in 2% of patients in group B NA treatment years 8-10. Combined biomarker endpoints were met at baseline and at years 1-4, 5-7, 8-10, and 11-14 of treatment by 3.3%, 12% and 14%, 13% and 38%, 26% and 29%, and 41% of patients, respectively.
Conclusions: HBV biomarker endpoints are associated with functional cure after the discontinuation of NA increase during long-term NA treatment.
Keywords: HBV biomarkers; HBcrAg; functional cure; stop NUC; treatment discontinuation.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Florian van Bömmel has served as a speaker for and provided consulting services to Gilead, Roche, Janssen, Ipsen, ADVANZ, Norgine, MSD, Esai, and AstraZeneca, and has served as an advisory board member of Janssen, Eisai, AstraZeneca, and Roche. He has received travel support from AstraZeneca, ADVANZ, and Gilead Sciences. He has received research funding from Gilead Sciences, Roche, VIR, Janssen, Ipsen, and Fujirebio. Pietro Lampertico: Advisory Board/Speaker Bureau for BMS, Roche, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Abbvie, MSD, Arrowhead, Alnylam, Janssen, Spring Bank, MYR, Eiger, Antios, Aligos, and Vir. Thomas Berg received grants from Abbvie, BMS, Gilead, MSD/Merck, Humedics, Intercept, Merz, Norgine, Novartis, Orphalan, and Sequana Medical and provided consulting services to Abbvie, Alexion, Bayer, Gilead, GSK, Eisai, Enyo Pharma, HepaRegeniX GmbH, Humedics, Intercept, Ipsen, Janssen, MSD/Merck, Novartis, Orphalan, Roche, Sequana Medical, SIRTEX, SOBI, and Shionogi. Thomas Berg has served as a speaker for Abbvie, Alexion, Bayer, Gilead, Eisai, Falk Foundation, Intercept, Ipsen, Janssen, MedUpdate GmbH, MSD/Merck, Novartis, Orphalan, Sequana Medica, SIRTEX, and SOBI and serves as an advisory board member for Gilead, Assembly, and GSK. All other authors disclose any conflicts of interest related to the present work.
Figures
References
-
- Lok AS. Chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1682–1683. - PubMed
-
- Polaris Observatory Collaborators. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:383–403. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017;67:370–398. - PubMed
-
- Jeng WJ, Lok AS. Should treatment indications for chronic hepatitis B be expanded? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:2006–2014. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

