A robust optimization model for allocation-routing problems under uncertain conditions
- PMID: 40378102
- PMCID: PMC12083844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322483
A robust optimization model for allocation-routing problems under uncertain conditions
Abstract
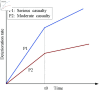
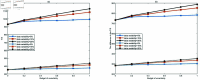
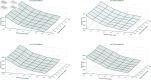
Post-earthquake emergency logistics faces significant challenges such as limited resources, uncertain casualty numbers, and time constraints. Developing a scientific and efficient rescue plan is crucial. One of the key issues is integrating facility location and casualty allocation in emergency medical services, an area rarely explored in existing research. This study proposes a robust optimization model to optimize the location of medical facilities and the transfer of casualties within a three-level rescue chain consisting of disaster areas, temporary hospitals, and general hospitals. The model accounts for limited medical resources, casualty classification, and uncertainty in casualty numbers. The Trauma Index Score (TIS) method is used to classify casualties into two groups, and the dynamic changes in their injuries after treatment at temporary hospitals are considered. The objective is to minimize the total TIS of all casualties. A robust optimization approach is applied to derive the corresponding robust model, and its validity is verified through case studies based on the Lushan earthquake. The findings show that data variability and the uncertainty budget play a critical role in determining hospital locations and casualty transportation plans. Temporary hospital capacity significantly influences the objective function more than general hospitals. As the problem size increases, the robust optimization model performs better than the deterministic model. Furthermore, uncertainty in casualty numbers has a more significant impact on serious casualties than moderate casualties. To enhance the model's applicability, it is extended into a two-stage dynamic location-allocation model to better address the complexity of post-disaster scenarios.
Copyright: © 2025 Zhang, Liu. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Robust optimization for casualty scheduling considering injury deterioration and point-edge mixed failures in early stage of post-earthquake relief.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 20;11:995829. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.995829. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36891349 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a Mass Casualty Surge Capacity Protocol for Emergency Medical Services to Use for Patient Distribution.South Med J. 2017 Dec;110(12):792-795. doi: 10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000740. South Med J. 2017. PMID: 29197316
-
A Geographic Simulation Model for the Treatment of Trauma Patients in Disasters.Prehosp Disaster Med. 2016 Aug;31(4):413-21. doi: 10.1017/S1049023X16000510. Epub 2016 May 25. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2016. PMID: 27221392
-
A systematic literature review of criteria and models for casualty distribution in trauma related mass casualty incidents.Injury. 2018 Nov;49(11):1959-1968. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Injury. 2018. PMID: 30220633
-
Preparing for a burn disaster in Brazil: Geospatial modelling to inform a coordinated response.Burns. 2023 Aug;49(5):1201-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2022.08.026. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Burns. 2023. PMID: 36195491 Review.
References
-
- Sun H, Wang Y, Zhang J, Cao W. A robust optimization model for location-transportation problem of disaster casualties with triage and uncertainty. Expert Syst Appl. 2021;175:114867. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114867 - DOI
-
- Sun H, Wang Y, Xue Y. A bi-objective robust optimization model for disaster response planning under uncertainties. Comput Ind Eng. 2021;155:107213. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107213 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

