The microRNA OsmiR393 regulates rice brown planthopper resistance by modulating the auxin-ROS signaling cross-talk
- PMID: 40378225
- PMCID: PMC12083543
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu6722
The microRNA OsmiR393 regulates rice brown planthopper resistance by modulating the auxin-ROS signaling cross-talk
Abstract
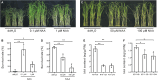
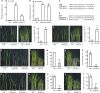
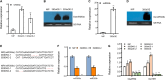
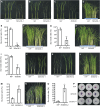
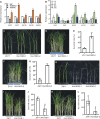
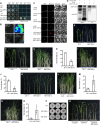
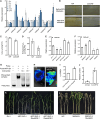
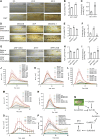
Auxin plays critical roles in plant development and stress response. However, the roles of auxin and the immune signaling factor, reactive oxygen species (ROS), in resistance to the brown planthopper (BPH), a notorious rice-specific piercing-sucking insect that causes severe yield losses, remain unclear. We revealed that moderate naphthalene acetic acid treatment activates rice resistance to BPH, BPH infestation induces ROS accumulation, and increase in ROS content promotes BPH resistance. Underlying these phenomena, the auxin receptors OsTIR1 and OsAFB2 positively, whereas the posttranscriptional regulator OsmiR393 negatively, regulate BPH resistance. Downstream of the OsmiR393/OsTIR1 module, through successive genetic function analysis of each gene, solid genetic relationship analysis, and various biochemical assays, we established an OsmiR393/OsTIR1-OsIAA10-OsARF12-OsRbohB genetic pathway that mediates BPH resistance, in which ROS are integral. Such cross-talk between auxin and ROS reveals the intricate signaling network underlying BPH resistance, which might assist with BPH resistance breeding.
Figures
References
-
- Min S., Lee S. W., Choi B.-R., Lee S. H., Kwon D. H., Insecticide resistance monitoring and correlation analysis to select appropriate insecticides against Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), a migratory pest in Korea. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 17, 711–716 (2014).
-
- Pieterse C. M., Van der Does D., Zamioudis C., Leon-Reyes A., Van Wees S. C., Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 28, 489–521 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Cance C., Martin-Arevalillo R., Boubekeur K., Dumas R., Auxin response factors are keys to the many auxin doors. New Phytol. 235, 402–419 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Wang D., Pei K., Fu Y., Sun Z., Li S., Liu H., Tang K., Han B., Tao Y., Genome-wide analysis of the auxin response factors (ARF) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Gene 394, 13–24 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

