Exploring the effect of multi-modal intervention against cognitive decline on atrophy and small vessel disease imaging markers in the AgeWell.de imaging study
- PMID: 40378769
- PMCID: PMC12144455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2025.103796
Exploring the effect of multi-modal intervention against cognitive decline on atrophy and small vessel disease imaging markers in the AgeWell.de imaging study
Abstract
Background: Multimodal lifestyle interventions might help to maintain healthy cognition in older age and to delay onset of dementia. Here, we studied the effects of a multi-modal lifestyle-based intervention, based on the FINGER trial, on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) markers of hippocampal-limbic atrophy and cerebral small vessel disease in older adults at increased risk for dementia in Germany.
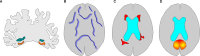
Methods: Leipzig participants of the multicenter AgeWell.de randomized controlled trial underwent neuroimaging before and after a two year intervention at 3 Tesla MRI. We extracted hippocampal volume and entorhinal cortex thickness (ECT), free water fraction (FW), peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity (PSMD), white matter hyperintensity volume and mean gray matter cerebral blood flow and assessed the effect of the intervention on these imaging markers using linear mixed models. We also tested the effect of the intervention on the hippocampus-dependent Mnemonic Similarity Test and fixel-based white matter microstructure.
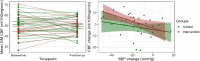
Results: 56 individuals (mean (sd) age: 68.8 (4.2) years, 26 females, 24/32 intervention/control group) were included at baseline and 41 returned after an average of 28 months for the second assessment. ECT and FW exhibited stronger decline in the intervention compared to the control group in preregistered models but not when adjusted for baseline differences. All other markers progressed similarly across groups, however sample size was smaller than expected. In exploratory analyses, cerebral blood flow increased more in the intervention group and this change was associated with decreases in systolic blood pressure.
Conclusions: In this group of older adults at risk for dementia, we find no conclusive evidence whether a multi-modal lifestyle intervention improves brain imaging markers of neurodegeneration and small vessel disease. Preliminary evidence suggested an association of the intervention, increased cerebral blood flow and systolic blood pressure reductions.
Abbreviations: ECT, entorhinal cortex thickness; FW, free water fraction; WHO, world health organization; AD, Alzheimer's disease; VCI, vascular cognitive impairment; FINGER, Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability; MTL, medial temporal lobe; MIND, Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay diet; cSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; WMH, white matter hyperintensities of presumed vascular origin; PSMD, peak width of the mean diffusivity distribution; WW-FINGERS, world wide FINGER studies; CAIDE, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Aging, and Incidence of Dementia; GPP, general practitioner praxis; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MST, Mnemonic Similarity Test; TE, echo time; TR, repetition time; FA, flip angle; FOV, field of view; GRAPPA, GeneRalized Autocalibrating Partial Parallel Acquisition; CMRR, Center for Magnetic Resonance Research; BOLD, blood oxygenation level dependent; pcASL: pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling; EPI, echo-planar imaging; FLAIR, fluid attenuated inversion recovery; CBF, cerebral blood flow; QA, quality assessment; GM, gray matter; HCV, hippocampal volume; eICV, estimated intracranial volume; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; MD, mean diffusivity; FA, fractional anisotropy TBSS: tract-based spatial statistics; CSF, cerebral spinal fluid; ISI, inter-stimulus interval; LDI, lure discrimination index; REC, recognition score; CG, control group; IG, intervention group; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment; CASMIN, Comparative Analysis of Social Mobility in Industrial Nations; BMI, body mass index; SBP/DBP, systolic/diastolic blood pressure; OSF, open science framework; LMM, linear mixed model; ANOVA, analysis of covariance.
Keywords: Cerebral Small Vessel Disease; Dementia; Hippocampus; Lifestyle; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Multi-component intervention.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017. Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017–2025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

