Enhanced delivery of camptothecin to colorectal carcinoma using a tumor-penetrating peptide targeting p32
- PMID: 40379119
- PMCID: PMC12182993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.05.036
Enhanced delivery of camptothecin to colorectal carcinoma using a tumor-penetrating peptide targeting p32
Abstract
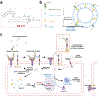
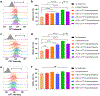
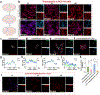
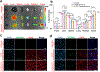
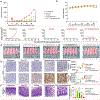
Camptothesome, a sphingomyelin (SM)-conjugated camptothecin (CPT) vesicular nanotherapeutic, addresses the poor solubility and lactone instability of CPT while enhancing drug loading, pharmacokinetics, and tumor distribution compared to CPT physically entrapped in conventional liposomes. Despite these improvements, the tumor uptake remains limited. To further enhance the tumor delivery efficiency and minimize the off-target distribution, we functionalize Camptothesome with the LinTT1 peptide, a CendR motif, which binds to overexpressed p32 proteins on tumor cell surface, initiating effective transcytosis for deep tumor penetration. Via systematic screening, the optimal peptide ratio on Camptothesome is identified. LinTT1/Camptothesome significantly increases cancer cell uptake without affecting normal cell internalization, resulting in enhanced anti-colorectal cancer cells activity. Additionally, decorating Camptothesome with the LinTT1 cell-penetrating peptide enables effective transcytosis via a Golgi-dependent intracellular trafficking mechanism, significantly improving the intratumoral delivery while reducing distribution to normal tissues. In a human HCT116 xenograft colorectal cancer (CRC) mouse model, LinTT1/Camptothesome demonstrates superior antitumor efficacy compared to both Camptothesome and Onivyde by upregulating cleaved caspase-3 and γH2AX. Our study substantiates the potential of leveraging a tumor-penetrating peptide to enhance the tumor delivery efficiency of Camptothesome, maximizing its therapeutic index for improved treatment of human CRC. STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE: Despite the improved tumor delivery achieved by Camptothesome, its tumor distribution and penetration remain limited. This is because the enhanced permeability and retention effect only facilitates nanotherapeutic distribution to tumor periphery through leaky vasculature. The C-end Rule (CendR) motif-neuropilin receptor system enhances tumor-homing peptides by binding to cellular surface receptors, triggering transcytosis. Herein, LinTT1, the most potent CendR peptide that binds to the overexpressed p32 receptor on cancer cells, was effectively engineered onto Camptothesome using thiol-maleimide lipid chemistry. The LinTT1/Camptothesome significantly enhanced tumor uptake and penetration while minimizing accumulation in normal tissues, demonstrating remarkable anticancer efficacy in a human xenograft colorectal cancer model. Our findings highlight the critical role of tumor-homing peptides in unlocking the full therapeutic potential of Camptothesome.
Keywords: Camptothesome; Colorectal cancer; Nanotherapeutics; Tumor-homing LinTT1 peptide; p32.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest J.L. has applied for patents related to the Camptothesome technology. The other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


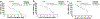
Similar articles
-
Camptothesome-based combination nanotherapeutic regimen for improved colorectal cancer immunochemotherapy.Biomaterials. 2024 Apr;306:122477. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122477. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Biomaterials. 2024. PMID: 38309054 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomal Vardenafil and Linagliptin Combined with Irinotecan for Synergistic Colorectal Cancer Therapy.Pharm Res. 2025 Jun;42(6):935-945. doi: 10.1007/s11095-025-03876-6. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Pharm Res. 2025. PMID: 40473893
-
Multi-Focused Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Modulation of Murine Hepatic Xenografts Enhances Nanoscale DOX@Lip Delivery and Therapeutic Effect.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 12;20:7359-7373. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S522247. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40529535 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

