Inhibiting peptidylarginine deiminases (PAD1-4) by targeting a Ca2+ dependent allosteric binding site
- PMID: 40379660
- PMCID: PMC12084562
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59919-4
Inhibiting peptidylarginine deiminases (PAD1-4) by targeting a Ca2+ dependent allosteric binding site
Abstract
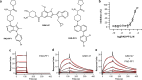
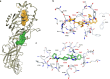
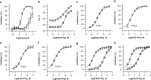
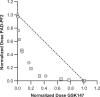
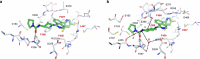
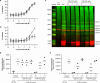
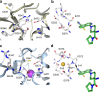
Peptidylarginine deiminases (PAD1-4) are calcium dependent enzymes responsible for protein citrullination, a post-translational modification converting arginine residues to citrulline. Elevated levels of citrullinated proteins have been associated with rheumatoid arthritis, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancers. Though highly selective PAD4 inhibitors have been described, inhibitors to the broader family currently are limited to covalent substrate analogs. Herein, we describe an allosteric binding pocket common to PAD1-4 suitable for the identification of potent, non-covalent enzyme inhibitors. A ligand-based virtual screen is utilized to identify a PAD4 inhibitor for which surface plasmon resonance confirms target binding but non-competitively with a known PAD4 ligand. We further show through co-crystal structure analysis that the ligand binds PAD4 at an allosteric pocket resulting in stabilization of a catalytically inactive, calcium-deficient enzyme conformation. A ligand designed based on this site potently inhibits all four PAD isozymes and prevents protein citrullination in neutrophils with a broader protein repertoire than observed with a PAD4-selective inhibitor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors were employees of Pfizer Inc. at the time this work was performed.
Figures
References
-
- Vossenaar, E. R. et al. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. BioEssays25, 1106–1118 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Taki, H. et al. Purification of enzymatically inactive peptidylarginine deiminase type 6 from mouse ovary that reveals hexameric structure different from other dimeric isoforms. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol.2, 304–310 (2011).
-
- Saijo, S. et al. Monomeric form of peptidylarginine deiminase type I revealed by x-ray crystallography and small-angle x-ray scattering. J. Mol. Biol.428, 3058–3073 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Funabashi, K. et al. Structures of human peptidylarginine deiminase type III provide insights into substrate recognition and inhibitor design. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.708, 108911 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

