A recombinant BCG with surface-displayed antigen induces humoral and cellular immune responses
- PMID: 40379714
- PMCID: PMC12084591
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00553-x
A recombinant BCG with surface-displayed antigen induces humoral and cellular immune responses
Abstract
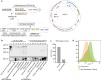
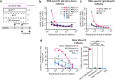
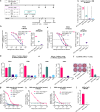
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is an attenuated vaccine widely used for tuberculosis prevention. While BCG has long been perceived as an intracellular candidate vector for delivering antigens against infectious diseases and cancers, challenges persist in inducing durable immune responses, particularly high-titer neutralizing antibodies (Nabs). Here we show that displaying antigens in the surface of BCG is a promising strategy to induce long-lasting Nabs production and T-cell responses. We constructed a recombinant BCG expressing the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) antigen on its cell wall, termed CW-rBCG::RBD, which achieved an antigen yield approaching 850 nanograms per 107 colony-forming unit. Compared with both the parental BCG and the RBD protein subunit vaccine (RBDAS01), intravenous administration of CW-rBCG::RBD followed by a booster dose significantly enhanced Nab production and increased the frequencies of RBD-specific central memory T cells (Tcm) and T follicular helper (Tfh) cells in the spleen. In mice primed with a single dose of CW-rBCG::RBD and boosted with RBDAS01, we also observed elevated Nab titers and detectable levels of RBD-specific IgG2a antibodies at 8 weeks post-priming, responses that were not observed in the BCG-primed or RBDAS01-only groups. Furthermore, subcutaneous co-administration of CW-rBCG::RBD and RBDAS01 sustained Nab production for up to 31 weeks and maintained higher Tfh and Tcm cell frequencies compared to both BCG co-administration with RBDAS01 and RBDAS01 alone. These findings highlight an effective strategy for optimizing BCG-based vaccination and immunotherapy platforms. Subject terms: recombinant BCG; immune response; vaccines; cell wall; SARS-CoV-2 RBD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Co-administration of recombinant BCG and SARS-CoV-2 proteins leads to robust antiviral immunity.Vaccine. 2024 Oct 3;42(23):126203. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.126203. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 39178767
-
Heterologous mRNA/MVA delivering trimeric-RBD as effective vaccination regimen against SARS-CoV-2: COVARNA Consortium.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2387906. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2387906. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 39087555 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 inducing multiepitopic and cross-reactive humoral neutralizing and cellular CD4 and CD8 responses.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1931-1946. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1978823. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 34538222 Free PMC article.
-
Protective immunity elicited by rBCG vaccines.Dev Biol Stand. 1994;82:163-70. Dev Biol Stand. 1994. PMID: 7958471 Review.
-
A Structural Landscape of Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 28;12:647934. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.647934. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Begnini, K. R., Buss, J. H., Collares, T. & Seixas, F. K. Recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG for immunotherapy in nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. APPL. MICROBIOL. BIOT. 99, 3741 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Uno-Furuta, S. et al. Immunization with recombinant Calmette-Guerin bacillus (BCG)-hepatitis C virus (HCV) elicits HCV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mice. VACCINE 21 3149 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

