Pancreas segmentation using AI developed on the largest CT dataset with multi-institutional validation and implications for early cancer detection
- PMID: 40379726
- PMCID: PMC12084540
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-01802-9
Pancreas segmentation using AI developed on the largest CT dataset with multi-institutional validation and implications for early cancer detection
Abstract
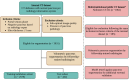
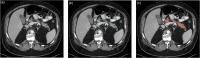
Accurate and fully automated pancreas segmentation is critical for advancing imaging biomarkers in early pancreatic cancer detection and for biomarker discovery in endocrine and exocrine pancreatic diseases. We developed and evaluated a deep learning (DL)-based convolutional neural network (CNN) for automated pancreas segmentation using the largest single-institution dataset to date (n = 3031 CTs). Ground truth segmentations were performed by radiologists, which were used to train a 3D nnU-Net model through five-fold cross-validation, generating an ensemble of top-performing models. To assess generalizability, the model was externally validated on the multi-institutional AbdomenCT-1K dataset (n = 585), for which volumetric segmentations were newly generated by expert radiologists and will be made publicly available. In the test subset (n = 452), the CNN achieved a mean Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 0.94 (SD 0.05), demonstrating high spatial concordance with radiologist-annotated volumes (Concordance Correlation Coefficient [CCC]: 0.95). On the AbdomenCT-1K dataset, the model achieved a DSC of 0.96 (SD 0.04) and a CCC of 0.98, confirming its robustness across diverse imaging conditions. The proposed DL model establishes new performance benchmarks for fully automated pancreas segmentation, offering a scalable and generalizable solution for large-scale imaging biomarker research and clinical translation.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Computed tomography; Pancreas; Volumetric segmentation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Volumetric Pancreas Segmentation on Computed Tomography: Accuracy and Efficiency of a Convolutional Neural Network Versus Manual Segmentation in 3D Slicer in the Context of Interreader Variability of Expert Radiologists.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2022 Nov-Dec 01;46(6):841-847. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001374. Epub 2022 Sep 1. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2022. PMID: 36055122 Free PMC article.
-
Two-stage deep learning model for fully automated pancreas segmentation on computed tomography: Comparison with intra-reader and inter-reader reliability at full and reduced radiation dose on an external dataset.Med Phys. 2021 May;48(5):2468-2481. doi: 10.1002/mp.14782. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33595105
-
Large-scale convolutional neural network for clinical target and multi-organ segmentation in gynecologic brachytherapy via multi-stage learning.Med Phys. 2025 Aug;52(8):e18067. doi: 10.1002/mp.18067. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40817425
-
Artificial intelligence-based models for quantification of intra-pancreatic fat deposition and their clinical relevance: a systematic review of imaging studies.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11808-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40682667 Review.
-
A systematic review on feature extraction methods and deep learning models for detection of cancerous lung nodules at an early stage -the recent trends and challenges.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Nov 20;11(1). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad9154. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024. PMID: 39530659
Cited by
-
Automated Quantitative Evaluation of Age-Related Thymic Involution on Plain Chest CT.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s10439-025-03805-z. Online ahead of print. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40684059
-
Artificial Intelligence-Augmented Imaging for Early Pancreatic Cancer Detection.Visc Med. 2025 May 28:1-9. doi: 10.1159/000546603. Online ahead of print. Visc Med. 2025. PMID: 40567392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Five-Year Pancreatic Cancer Survival Rate Increases to 12% https://pancan.org/news/five-year-pancreatic-cancer-survival-rate-increa....
-
- Siegel, R. L., Giaquinto, A. N. & Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin.74, 12–49. 10.3322/caac.21820 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Holly, E. A., Chaliha, I., Bracci, P. M. & Gautam, M. Signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer: A population-based case-control study in the San Francisco Bay area. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.2, 510–517. 10.1016/s1542-3565(04)00171-5 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

