An AI-based automatic leukemia classification system utilizing dimensional Archimedes optimization
- PMID: 40379734
- PMCID: PMC12084586
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98400-6
An AI-based automatic leukemia classification system utilizing dimensional Archimedes optimization
Abstract
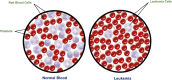
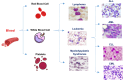
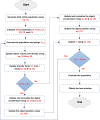
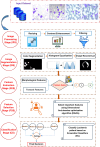
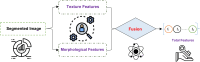
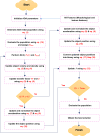
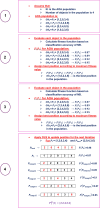
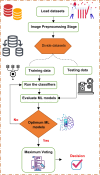
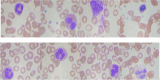
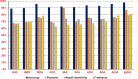
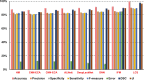
Leukemia is a common type of blood cancer marked by the abnormal and uncontrolled proliferation and expansion of white blood cells. This anomaly impacts the blood and bone marrow, diminishing the bone marrow's capacity to generate platelets and red blood cells. Abnormal red blood cells in the bloodstream harm various organs, such as the kidneys, liver, and spleen. Detection and classification of infected patients at an early stage can save their lives. In this paper, a new Artificial Intelligence (AI) system is proposed. The proposed system is called Leukemia Classification System (LCS). The proposed LCS composed of five stages, which are; (i) Image Processing Stage (IPS), (ii) Image Segmentation Stage (ISS), (iii) Feature Extraction Stage (FES), (iv) Feature Selection Stage (FSS), and (v) Classification Stage (CS). During IPS, the input images are preprocessed through several processes: resizing, enhancement, and filtering. Next, the preprocessed images are segmented through ISS. Then, two types of features, texture and morphological features, are extracted. We feed these extracted features to FSS, which uses a proposed method to select the most important and effective features. The proposed method is called the Dimensional Archimedes Optimization Algorithm (DAOA). DAOA is based on the Archimedes Optimization Algorithm (AOA) and Dimensional Learning Strategy (DLS). Actually, DLS transmits valuable information about the ideal position of the population in every generation to the personal best position of each individual particle. This improves both the precision and efficiency of convergence while reducing the likelihood of the "two steps forward, one step back" phenomenon. This problem offers a more precise solution. Finally, these selected features are fed to the proposed classification model. Experimental results show that the proposed LCS outperforms the others.
Keywords: Classification; Feature selection; Leukemia; Machine learning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Figures



References
-
- Ramaneswaran, S., Srinivasan, K., Vincent, P. D. & Chang, C. Y. Hybrid inception v3 XGBoost model for acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification. Comput. Math. Methods Med.1, 2577375. 10.1155/2021/2577375 (2021). - DOI
-
- Ghaderzadeh, M. et al. Machine learning in detection and classification of leukemia using smear blood images: A systematic review. Sci. Program.2021, 9933481. 10.1155/2021/9933481 (2021). - DOI
-
- Imran, T. et al. Malaria blood smear classification using deep learning and best features selection. Comput. Mater. Contin.70, 1875–1891. 10.32604/cmc.2022.018946 (2022). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

