Habitat-based radiomics from contrast-enhanced CT and clinical data to predict lymph node metastasis in clinical N0 peripheral lung adenocarcinoma ≤ 3 cm
- PMID: 40379768
- PMCID: PMC12084560
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02181-x
Habitat-based radiomics from contrast-enhanced CT and clinical data to predict lymph node metastasis in clinical N0 peripheral lung adenocarcinoma ≤ 3 cm
Abstract
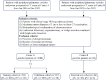
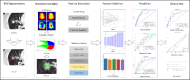
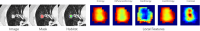
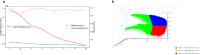
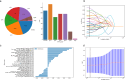
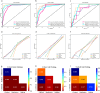
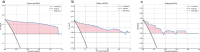
This study aims to develop an integrated model combining habitat-based radiomics and clinical data to predict lymph node metastasis in patients with clinical N0 peripheral lung adenocarcinomas measuring ≤ 3 cm in diameter. We retrospectively analyzed 1132 patients with lung adenocarcinoma from two centers who underwent surgical resection with lymph node dissection and had preoperative computed tomography (CT) scans showing peripheral nodules ≤ 3 cm. Multivariable logistic regression was employed to identify independent risk factors for the clinical model. Radiomics and habitat models were constructed by extracting and analyzing radiomic features and habitat regions from contrast-enhanced CT images. Subsequently, a combined model was developed by integrating habitat-based radiomic features with clinical characteristics. Model performance was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). The habitat model exhibited promising predictive performance for lymph node metastasis, outperforming other standalone models with AUCs of 0.962, 0.865, and 0.853 in the training, validation, and external test cohorts, respectively. The combined model demonstrated superior discriminative ability, achieving the highest AUCs of 0.983, 0.950, and 0.877 for the training, validation, and external test cohorts, respectively. The integration of habitat-based radiomic features with clinical data offers a non-invasive approach to assess the risk of lymph node metastasis, potentially supporting clinicians in optimizing patient management decisions.
Keywords: Habitat imaging; Lymph node metastasis; Peripheral lung adenocarcinomas; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

