Diagnostic and prognostic roles of endothelial- and platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 40380176
- PMCID: PMC12085008
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06522-2
Diagnostic and prognostic roles of endothelial- and platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
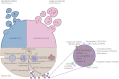
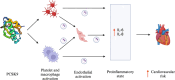
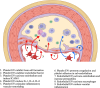
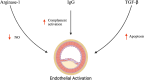
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-bound structures released by all cell types. They play a critical role in intercellular communication by transferring their cargo, comprising proteins, lipids, metabolites, RNAs, miRNAs, and DNA fragments, to recipient cells. This transfer influences gene expression, signaling pathways, and cellular behavior. Due to their ability to alter the physiology of recipient cells, EVs hold significant therapeutic potential. Additionally, EVs are implicated in various physiological and pathological processes, including immune regulation, cancer progression, and cardiovascular diseases. EVs have been detected in many biological fluids, such as peripheral blood, saliva, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and breast milk. The cargo of EVs dynamically reflects the physiological and pathological state of their parent cells, making them promising candidates for liquid biopsies in various clinical conditions. Specifically, different EV subtypes in cardiovascular diseases have been studied, with both endothelial and platelet-derived EVs playing significant roles in cardiovascular pathologies. This review focuses on the diagnostic and prognostic potential of endothelial and platelet-derived EVs in cardiovascular diseases, highlighting the role of EV subpopulations.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Endothelial-derived extracellular vesicles; Extracellular vesicles; Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable (review). Consent for publication: Not applicable (review). Competing interests: RC has developed multiple EV-associated patents for putative clinical utilization: US20200088734 A1, United States; WO2020146390 A1, WIPO (PCT). RC owns equity in Exocure Bioscience Inc. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brocco D, De Bellis D, Di Marino P, et al. High blood concentration of leukocyte-derived extracellular vesicles is predictive of favorable clinical outcomes in patients with pancreatic cancer: results from a multicenter prospective study. Cancers (Basel). 2022. 10.3390/cancers14194748. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

