Fe3O4@SiO2-SnCl4-promoted synthesis, cytotoxic evaluation, molecular docking, and MD simulation of some indenopyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives
- PMID: 40380230
- PMCID: PMC12085073
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-025-01489-z
Fe3O4@SiO2-SnCl4-promoted synthesis, cytotoxic evaluation, molecular docking, and MD simulation of some indenopyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives
Abstract
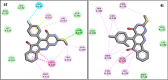
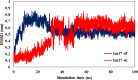
In this study, an efficient and environmentally friendly method for the one-pot synthesis of indenopyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives was developed using Fe3O4@SiO2-SnCl4 nanoparticles as a catalyst. Indenopyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines (4a-4j) were synthesized via three-component couplings of 6-amino-2-(methylthio)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one, 1,3-indanedione, and aldehydes in water as the solvent. In this reaction, Fe3O4@SiO2-SnCl4 demonstrated a highly catalytic nature, an easy handling procedure, short reaction times, recyclability exploitation, and excellent yields. The cytotoxic activities of the synthesized indenopyrido[2,3-d] pyrimidines analogues were evaluated against three cancer cell lines; MCF-7 (breast carcinoma), A549 (lung non-small cell carcinoma), and SKOV3 (ovarian carcinoma) using MTT assay. Additionally, molecular docking studies and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of the investigated compounds was performed to verify their binding modes toward EGFR kinase receptor as the possible targets. This analysis aimed to predict the antitumor mechanisms of the synthesized compounds. The binding free energy values of the compounds showed a satisfactory correlation with their cytotoxic activities.
Keywords: Cytotoxic activity; Indenopyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine; MD Simulation; Molecular docking.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Zheng L-W, et al. Synthesis of novel oxime-containing pyrazole derivatives and discovery of regulators for apoptosis and autophagy in A549 lung cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010;20(16):4766–70. - PubMed
-
- Patrick GL. An introduction to medicinal chemistry. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2013.
-
- DeGraw JI, et al. Antimicrobial activity of 8-deazafolic acid. J Med Chem. 1974;17(4):470–1. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto J, Minami S. Pyrido [2, 3-d] pyrimidine antibacterial agents 3 8-alkyl-and 8-vinyl-5, 8-dihydro-5-oxo-2-(1-piperazinyl) pyrido [2, 3-d] pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acids and their derivatives. J Med Chem. 1975;18(1):74–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
