MAKO robotic-assisted compared to conventional total hip arthroplasty for hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40380310
- PMCID: PMC12083021
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-025-05866-1
MAKO robotic-assisted compared to conventional total hip arthroplasty for hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) is the gold standard for treating end-stage hip osteoarthritis. Robotic-assisted systems, particularly the MAKO system, have been introduced to enhance reproducibility and safety. However, meta-analyses comparing MAKO-assisted THAs (MAKO-THA) to conventional methods are lacking, and previous reviews often aggregate various indications, introducing heterogeneity.
Methods: A random-effects meta-analysis was conducted on comparative studies between MAKO robotic-arm-assisted and conventional THAs in patients undergoing THA for solely hip osteoarthritis. Clinical outcomes (Harris Hip Scores [HHS], Forgotten Joint Scores [FJS], and Oxford Hip Scores [OHS]), radiographic parameters (implant positioning accuracy), leg-length-discrepancy, surgical duration, and complications were evaluated.
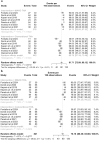
Results: 20 comparative studies were included. MAKO-assisted THAs resulted in higher postoperative HHS (MAKO-THA: 89.1, 95%CI: 86.4-91.7; C-THA: 87.0, 95%CI: 83.8-90.1), FJS (MAKO-THA: 84.7, 95%CI: 79.9-89.6; C-THA: 74.9, 95%CI: 64.0-95.7), and OHS (MAKO-THA: 89.1, 95%CI: 86.4-91.7; C-THA: 87.0, 95%CI: 83.8-90.1). FJS and OHS improvements were significantly greater compared to conventional THA (HHS WMD 2.2 [95%CI: -0.3-4.7, p = 0.09; FJS WMD: 8.7 [95%CI: 2.7-14.8], p = 0.005; OHS WMD: 1.5 [95% CI: 0.1-2.8], p = 0.03). MAKO-THA resulted in 94.7% and 90.3% of implants positioned within Lewinnek-and-Callanan zones, respectively, compared to 65.8% and 57.1% in conventional THA. MAKO-THA had longer mean surgical durations and lower postoperative leg-length discrepancy, but not significantly (Surgical Duration WMD: 3.5 [95%CI: -2.5-9.5], p = 0.3; Leg Length Discrepancy WMD: -0.2 [95%CI: -0.7-0.4], p = 0.6). Complication rates were low and non-significant (MAKO-THA: 3.0% [95%CI: 1.2-7.4]; C-THA: 3.5% [95% CI: 1.2-10.1), p = 0.3).
Conclusion: MAKO robotic-arm-assisted THA significantly improves Forgotten Joint Scores, Oxford Hip Scores and reproducibility in implant positioning without compromising on surgical duration and complication rates.
Protocol registration: CRD42024542794.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Hip osteoarthritis; Meta-analysis; Orthopaedic surgery; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors provided critical conceptual input, interpreted the data analysis, read and approved the final draft of the manuscript have accessed and verified the data. were responsible for the decision to submit the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



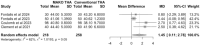




References
-
- Alessio-Mazzola M, Colombo P, Barducci N, Ghezzi E, Zagra L, Caldora P, et al. Direct anterior approach with conventional instruments versus robotic posterolateral approach in elective total hip replacement for primary osteoarthritis: a case-control study. J Orthop Traumatol. 2024;25(1):9. 10.1186/s10195-024-00753-7. PMID: 38381320; PMCID: PMC10881946. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banchetti R, Burco N, Sciulli L, Vicentini R. Comparison of conventional versus robotic-assisted total hip arthroplasty using the Mako system: an Italian retrospective study. J Arthritis. 2018;7:1–4.
-
- Bargar WL, Bauer A, Börner M. Primary and revision total hip replacement using the Robodoc system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(354):82–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

