Biosourced Functional Hydroxybenzoate- co-Lactide Polymers with Antimicrobial Activity
- PMID: 40380948
- PMCID: PMC12147117
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c04624
Biosourced Functional Hydroxybenzoate- co-Lactide Polymers with Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
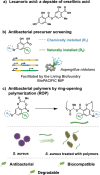
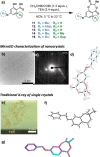
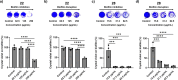
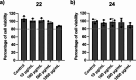
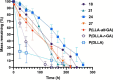
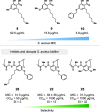
Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global health challenge, and compounds that address this issue have attracted significant attention. In particular, bioderived molecules that possess natural antimicrobial properties can be useful to prepare active macromolecules that are degradable. In this work, a 4-(methyl/allyl/benzyl)oxy-6-(H/alkyl)-2-oxy-benzoate-co-lactide-based polymer library was designed and studied for antimicrobial activity. The monomer precursors were heterologously produced and purified from an engineered fungal host, chemically modified with 4-(methyl/allyl/benzyl)oxy substituents, and ring-closed to form the 3-methyl-5H-benzo[e][1,4]dioxepine-2,5(3H)-diones. The polymers were synthesized by ring-opening polymerization using a 3-O urea/1-methyl-2,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-pyrimido[1,2-a]pyrimidine catalytic system and 3-methyl-butan-1-ol as the initiator. Polymers at different degrees of polymerization were prepared by varying the [monomer]/[initiator] (M/I = 5-30) and tested for activity against the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Polymers were identified that were antimicrobial and disrupted biofilms while maintaining good in vitro biocompatibility. The degradability of the polymers was confirmed. Overall, these results demonstrate the power of utilizing a combination of synthetic biology and chemistry to produce functional and degradable polymers that are potent inhibitors of the Gram-positive bacterium S. aureus, with potential applications in medicine.
Figures
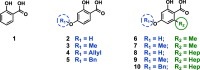

References
-
- 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report | CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html (accessed Dec 11, 2024).
-
- Pham P., Oliver S., Boyer C.. Design of Antimicrobial Polymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023;224(3):2200226. doi: 10.1002/macp.202200226. - DOI
-
- Fleming A.. On the Antibacterial Action of Cultures of a Penicillium, with Special Reference to Their Use in the Isolation of B. Influenzæ. Br. J. Exp. Biol. 1929;10(3):226–236.
-
- Schmidt N. W., Mishra A., Lai G. H., Davis M., Sanders L. K., Tran D., Garcia A., Tai K. P., McCray P. B., Ouellette A. J., Selsted M. E., Wong G. C. L.. Criterion for Amino Acid Composition of Defensins and Antimicrobial Peptides Based on Geometry of Membrane Destabilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133(17):6720–6727. doi: 10.1021/ja200079a. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

