Plasmonic coffee-ring biosensing for AI-assisted point-of-care diagnostics
- PMID: 40382337
- PMCID: PMC12085679
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59868-y
Plasmonic coffee-ring biosensing for AI-assisted point-of-care diagnostics
Abstract
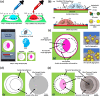
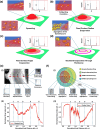
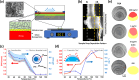
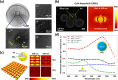
A major challenge in addressing global health issues is developing simple, affordable biosensors with high sensitivity and specificity. Significant progress has been made in at-home medical detection kits, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, we demonstrated a coffee-ring biosensor with ultrahigh sensitivity, utilizing the evaporation of two sessile droplets and the formation of coffee-rings with asymmetric nanoplasmonic patterns to detect disease-relevant proteins as low as 3 pg/ml, under 12 min. Experimentally, a protein-laden droplet dries on a nanofibrous membrane, pre-concentrating biomarkers at the coffee ring. A second plasmonic droplet with functionalized gold nanoshells is then deposited at an overlapping spot and dried, forming a visible asymmetric plasmonic pattern due to distinct aggregation mechanisms. To enhance detection sensitivity, a deep neural model integrating generative and convolutional networks was used to enable quantitative biomarker diagnosis from smartphone photos. We tested four different proteins, Procalcitonin (PCT) for sepsis, SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid (N) protein for COVID-19, Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) for cancer diagnosis, showing a working concentration range over five orders of magnitude. Sensitivities surpass equivalent lateral flow immunoassays by over two orders of magnitude using human saliva samples. The detection principle, along with the device, and materials can be further advanced for early disease diagnostics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liquid-metal-based microfluidic nanoplasmonic platform for point-of-care naked-eye antibody detection.Biosens Bioelectron. 2024 Oct 1;261:116469. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116469. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Biosens Bioelectron. 2024. PMID: 38850738
-
Ultrasensitive Love-SAW Biosensor Based on Self-Assembled DMSN@AuNPs with In Situ Amplification for Detecting Biomarker Procalcitonin in Exhaled Breath Condensate.ACS Sens. 2025 Apr 25;10(4):2994-3002. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.5c00021. Epub 2025 Apr 7. ACS Sens. 2025. PMID: 40192343
-
Colorimetric Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Plasmonic Biosensors and Smartphones.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Dec 14;14(49):54527-54538. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c15407. Epub 2022 Dec 1. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 36454041
-
Emerging Trends of Gold Nanostructures for Point-of-Care Biosensor-Based Detection of COVID-19.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;67(4):1398-1422. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01157-y. Epub 2024 May 4. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38703305 Review.
-
Innovative strategies for enhancing AuNP-based point-of-care diagnostics: Focus on coronavirus detection.Talanta. 2025 Apr 1;285:127362. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.127362. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 39675069 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

