Transcriptome of Taenia solium during in vitro cyst activation and initial growth into the tapeworm stage
- PMID: 40382389
- PMCID: PMC12085659
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05141-2
Transcriptome of Taenia solium during in vitro cyst activation and initial growth into the tapeworm stage
Abstract
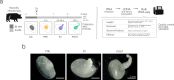
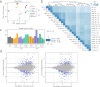
The cestode Taenia solium develops as a tapeworm solely in the human intestine, starting from a larva (cyst). Upon maturing, it produces hundreds of thousands of infectious eggs. When ingested by pigs or humans, the eggs develop as cysts that lodge in various tissues, including the brain, leading to neurocysticercosis. Despite advances in understanding cestode biology through genomic and transcriptomic studies, particularly in model organisms, much remains unknown about the activation of T. solium cysts in the human digestive tract and the events that drive the development into adult worms-the stage responsible for dispersing the parasite. We present a transcriptome generated by Next Generation Sequencing from T. solium cysts activated in culture and collected at three different in vitro growth phases, defined by their morphology. Differentially expressed genes and biological processes relevant to activation and growth can be explored with the dataset. The information is valuable for identifying genes that regulate the molecular, metabolic, and cellular events leading to parasite maturation or elements driving its transmission.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial relationship between Taenia solium tapeworm carriers and necropsy cyst burden in pigs.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Apr 13;11(4):e0005536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005536. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28406898 Free PMC article.
-
Increased iron uptake in the bladder wall of racemose cysts of Taenia solium.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2022 Sep;251:111496. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2022.111496. Epub 2022 Jul 10. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35830923 Free PMC article.
-
Taenia solium taeniasis/cysticercosis: From parasite biology and immunology to diagnosis and control.Adv Parasitol. 2021;112:133-217. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2021.03.003. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Adv Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34024358
-
Transmission dynamics of Taenia solium and potential for pig-to-pig transmission.Parasitol Int. 2006;55 Suppl:S131-5. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.021. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Parasitol Int. 2006. PMID: 16352459 Review.
-
Zoonotic Taenia infections with focus on cysticercosis due to Taenia solium in swine and humans.Res Vet Sci. 2021 Jan;134:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.11.015. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Res Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33321377 Review.
References
-
- Donadeu, M. et al. WHO Taenia Solium Endemicity Map – 2022 Update. 4https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-wer9717-169-172 (2022).
-
- WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007-2015. https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/199350 (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2015).
-
- Campbell, W. C. The Efficacy of Surface-Active Agents in Stimulating the Evagination of Cysticerci In vitro. J. Parasitol.49, 81, 10.2307/3275679 (1963). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

