Computational exploration of Eucommia ulmoides flavonoids as potential RANKL inhibitors via molecular docking and dynamics simulations
- PMID: 40382406
- PMCID: PMC12085681
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-01913-3
Computational exploration of Eucommia ulmoides flavonoids as potential RANKL inhibitors via molecular docking and dynamics simulations
Abstract
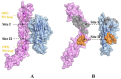
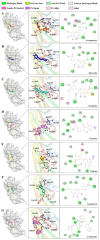
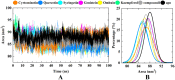
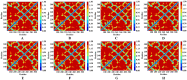
Osteoporosis, characterized by excessive osteoclast activation, is mediated through the RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling axis. While flavonoids from Eucommia ulmoides (EU) have demonstrated anti-osteoclastogenic activity, their atomic-level mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we investigated six EU-derived flavonoids (cyrtominetin, quercetin, syringetin, genistein, ombuin, and kaempferol) targeting RANKL using integrated computational approaches. Molecular docking revealed strong binding affinities (Total_Score > 4.0) for all compounds, with cyrtominetin exhibiting the highest affinity (-50.205 kJ/mol via MM-PBSA), primarily through hydrogen bonds with Gly178, His180, Lys181, and Asn295. Moreover, most flavonoids interacted with RANKL by forming strong hydrogen bonds with Gly178 and Asn295, exhibiting higher binding affinity that was identified as essential for the activity. All-atom molecular dynamics simulations (100 ns) confirmed complex stability, demonstrating: low RMSD fluctuations (< 4.0 Å) and compact Rg values (16.0-17.0 Å). Notably, binding free energy decomposition identified both electrostatic and van der Waals contributions as critical for stabilization. These results identify cyrtominetin as a promising lead compound for RANKL inhibition, providing structural insights for designing flavonoid-based therapeutics against osteoporosis.
Keywords: Flavonoids; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics; Osteoporosis; RANKL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Identification of potential inhibitors against Corynebacterium diphtheriae MtrA response regulator protein; an in-silico drug discovery approach.J Mol Graph Model. 2024 Dec;133:108858. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2024.108858. Epub 2024 Sep 1. J Mol Graph Model. 2024. PMID: 39232488
-
Computational insights into flavonoids inhibition of dengue virus envelope protein: ADMET profiling, molecular docking, dynamics, PCA, and end-state free energy calculations.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 9;20(7):e0327862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327862. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40632786 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Type II Diabetes Inhibitors from Genus Daphne Plant-species: An Integrated Computational Study.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(8):1413-1442. doi: 10.2174/0113862073262227231005074024. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38584562
-
Bisphosphonates or RANK-ligand-inhibitors for men with prostate cancer and bone metastases: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 3;12(12):CD013020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33270906 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Integrating multi-dimensional data to reveal the mechanisms and molecular targets of baikening granules for treatment of pediatric influenza.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 11;12:1637980. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1637980. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40718794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gullberg, B., Johnell, O. & Kanis, J. A. World-Wide projections for hip fracture. Osteoporos. Int.7, 407–413 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Kanis, J. A. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: Synopsis of a WHO report. WHO Study Group. Osteoporos. Int.4, 368–381 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Kim, B., Lee, K. Y. & Park, B. Icariin Abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-Mediated TRAF6/NF-Kappab/ERK Signaling Pathway in Raw264.7 Cells. Phytomedicine51, 181–190 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

