The effects of policosanol supplementation on creatinine: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40382621
- PMCID: PMC12085850
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-025-04911-0
The effects of policosanol supplementation on creatinine: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: Policosanol, a compound generated from sugar cane, consists of alcohols such as octacosanol, hexacosanol, and triacontanol, which possess antioxidant properties. Evaluating the impact of this antioxidant on serum creatinine in clinical settings is essential because of the contradictory findings. This comprehensive review and dose-response meta-analysis attempts to evaluate the impact of policosanol supplementation on creatinine levels.
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed in bibliographic databases such as Cochrane, PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science, covering the period from inception to November 2023. The necessary data was retrieved, and pertinent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that satisfied the inclusion criteria were included. Weighted mean differences (WMDs) were the reported measure of the pooled effects. To find between-study heterogeneities, the I-squared test was employed.
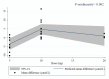
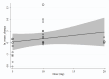
Results: A total of 2427 participants were involved in the twenty-one RCTs that were included. A meta-analysis showed that policosanol had no significant change in creatinine levels in participants consuming policosanol compared to placebo consumers (WMD = 0.21 µmol/l; 95% CI = - 0.85 to 1.26; P = 0.70). Policosanol consumption for durations ≥ 24 weeks significantly decreased creatinine, according to subgroup studies. There was a non-linear correlation between changes in creatinine levels and the dosage of prescription policosanol (P non_linearity = 0.002). However, the treatment time did not have a significant impact on creatinine levels in a non-linear manner (P non_linearity = 0.24).
Conclusion: Policosanol supplementation has no significant effect on creatinine levels.
Keywords: Creatinine; Meta-analysis; Policosanol; Randomized controlled trials.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Policosanol supplementation significantly improves blood pressure among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2019 Aug;45:89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 May 23. Complement Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31331588
-
The effect of Nigella sativa on the measures of liver and kidney parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jun;156:104767. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104767. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32201245
-
Efficacy and safety of sugarcane policosanol on dyslipidemia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018 Jan;62(1). doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700280. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018. PMID: 28730734
-
Effects of a nutraceutical combination containing berberine (BRB), policosanol, and red yeast rice (RYR), on lipid profile in hypercholesterolemic patients: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2016 Jul-Aug;28(4):178-87. doi: 10.1016/j.arteri.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2016. PMID: 27131395
-
Policosanol composition, antioxidant and anti-arthritic activities of milk thistle (Silybium marianum L.) oil at different seed maturity stages.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Apr 16;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0682-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29661192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brosnan JT, Brosnan ME. Creatine metabolism and the urea cycle. Mol Genet Metab. 2010;100:S49–52. - PubMed
-
- Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2000;80(3):1107–213. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D, et al. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130(6):461–70. - PubMed
-
- Kashani KB, Frazee EN, Kukrálová L, Sarvottam K, Herasevich V, Young PM, et al. Evaluating muscle mass by using markers of kidney function: development of the sarcopenia index. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(1):e23–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

