The regulation of LRPs by miRNAs in cancer: influencing cancer characteristics and responses to treatment
- PMID: 40382654
- PMCID: PMC12085831
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03804-z
The regulation of LRPs by miRNAs in cancer: influencing cancer characteristics and responses to treatment
Abstract
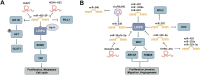
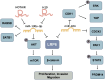
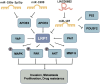
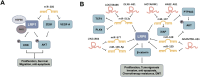
The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) family is a group of cell surface receptors that participate in a variety of biological processes, including lipid metabolism, Wnt signaling, and bone metabolism. miRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression and play a role in many biological processes, including the occurrence and development of tumors. Accumulating evidence demonstrates that LRP members are modulated by miRNAs across multiple cancer types, influencing key oncogenic processes-including tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis suppression, extracellular matrix remodeling, cell adhesion, and angiogenesis. The LRPs, miRNAs, their upstream lncRNAs, and downstream signaling molecules often form complex signaling pathways to regulate the activity of tumor cells. However, the tissue-specific roles and mechanistic underpinnings of these pathways remain incompletely understood. When examining the emerging concept of the interaction between miRNAs and LRPs, we emphasize the significance of these complex regulatory layers in the initiation and progression of cancer. Collectively, these findings are critical for advancing our understanding of the role of the LRPs family in the occurrence and development of tumors, as well as for the development of new strategies for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; CircRNAs; LRPs; LncRNA; miRNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
LRP-1 and LRP-2 receptors function in the membrane neuron. Trafficking mechanisms and proteolytic processing in Alzheimer's disease.Front Physiol. 2012 Jul 16;3:269. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00269. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22934024 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptors, LRPs, and Lipoproteins in Pulmonary Hypertension.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2022 Feb 28;7(2):164-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.09.011. eCollection 2022 Feb. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35257044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressive Long Non-Coding RNA-microRNA-Messenger RNA Regulatory Axes Identified by Analyzing Multiple Platform Omics Data from Cr(VI)-Transformed Cells and Their Implications in Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 20;10(10):2334. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102334. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289596 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks during osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jun 7;23(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08646-x. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35672672 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory miRNAs, circRNAs and lncRNAs in cell cycle progression of breast cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Jul 11;23(3):233. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01130-z. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37432486 Review.
References
-
- Gonias SL, Gaultier A, Jo M. Regulation of the urokinase receptor (uPAR) by LDL receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1). Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(19):1962–9. - PubMed
-
- Lindner I, Hemdan NY, Buchold M, Huse K, Bigl M, Oerlecke I, et al. Alpha2-macroglobulin inhibits the malignant properties of Astrocytoma cells by impeding beta-catenin signaling. Cancer Res. 2010;70(1):277–87. - PubMed
-
- Zhou X, Xia E, Bhandari A, Zheng C, Xiang J, Guan Y, et al. LRP4 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion in papillary thyroid cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(1):257–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

