Extraction and Characterization of Phenolic Acid Compounds of Zahidi and Khastawi Dates Seed Extract and Evaluation of their Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 40382693
- PMCID: PMC12085802
- DOI: 10.34172/aim.33929
Extraction and Characterization of Phenolic Acid Compounds of Zahidi and Khastawi Dates Seed Extract and Evaluation of their Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
Background: The date fruit is a remarkable source of nutraceuticals and bioactive compounds. Different types of phenolic compounds with high antioxidant capacity are found in date seed extract. Additionally, these compounds can be potential antibacterial agents to combat antibiotic resistance strains. Therefore, the main idea of the current study was to quantify five key phenolic acids in the ethanolic extract of Zahidi and Khastawi dates seed and to examine their antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
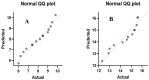
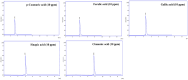
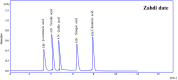
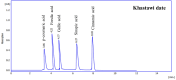
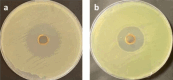
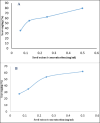
Methods: The concentration of gallic acid, ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, sinapic acid and cinnamic acid in the seed extracts were determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Then, antibacterial activity of date seed extracts was analyzed using well diffusion method. Furthermore, a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed to confirm the antibacterial effects of the seed extracts.
Results: Phenolic acids were found to be in the range of 10.59 to 33.65 µg mg-1 in Zahidi and 13.69 to 41.56 µg mg-1 in Khastawi date seed extract. Gallic acid was the dominant phenolic acid, while cinnamic acid was seen in the lowest concentrations compared with the other phenolic acids in both cultivars. Antibacterial activity study showed that the growth inhibition effect of Khastawi date (14±0.21 mm) was higher than that of Zahidi date (8±0.13 mm) against MRSA. As well, the maximum DPPH scavenging percentage was 79% and 62% for the Khastawi and Zahidi date seed extracts, respectively. Also, SEM analysis suggested that treatment of MRSA with date seed extract resulted in a significant disruption of bacterial structure.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that date seed extract can be considered as a potential source of antibacterial compounds for the drug discovery purposes.
Keywords: Date seed; Drug resistance; Methicillin-resistant; Phenolic acid; Staphylococcus aureus.
© 2025 The Author(s). This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unveiling phenolic content, antibacterial, and antibiofilm potential of sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) seed shell extracts against Staphylococcus aureus.PeerJ. 2025 Jun 4;13:e19524. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19524. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40511378 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory potential of Thai mango seed kernel extract against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Molecules. 2011 Jul 25;16(8):6255-70. doi: 10.3390/molecules16086255. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21788933 Free PMC article.
-
Prunus persica var. platycarpa (Tabacchiera Peach): Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Pulp, Peel and Seed Ethanolic Extracts.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2015 Sep;70(3):331-7. doi: 10.1007/s11130-015-0498-1. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26138775
-
Evaluation of phenolic profile, enzyme inhibitory and antimicrobial activities of Nigella sativa L. seed extracts.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2017 Nov 20;17(4):286-294. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2017.2049. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28590231 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Prepared from Camellia Sinensis Extracts in Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2024 Nov 11;58(6):659-676. doi: 10.33594/000000741. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39535105
References
-
- Echegaray N, Gullón B, Pateiro M, Amarowicz R, Misihairabgwi JM, Lorenzo JM. Date fruit and its by-products as promising source of bioactive components: a review. Food Rev Int. 2023;39(3):1411–32. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2021.1934003. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials