Identification of hub biomarkers in coronary artery disease patients using machine learning and bioinformatic analyses
- PMID: 40383719
- PMCID: PMC12086195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02123-7
Identification of hub biomarkers in coronary artery disease patients using machine learning and bioinformatic analyses
Abstract
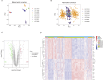
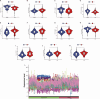
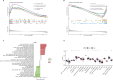
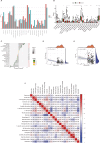
Understanding the molecular underpinnings of CAD is essential for developing effective therapeutic strategies. This study aims to identify and analyze differentially expressed hub biomarkers in the peripheral blood of CAD patients. Based on RNA-seq datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, machine learning algorithms including LASSO, RF, and SVM-RFE were applied. Furthermore, the hub biomarkers were enriched to ascertain their roles in immune cell expression and signaling pathways through GO, KEGG, GSVE, and GSVA. An in vivo experiment was conducted to verify the hub biomarkers. Eleven hub biomarkers (ITM2B, GNA15, PLAU, GNG11, HIST1H2BH, SLC11A1, RPS7, DDIT4, CD83, GNLY, and S100A12) were identified and associated with CD8 + T cells and NK cells. They were mainly involved in immune responses, cardiac muscle contraction, oxidative phosphorylation, and apoptotic signaling pathways. Moreover, ITM2B had the most importance and significance to be the biomarker of CAD patients. In conclusion, these findings point to the possibility of ITM2B as a biomarker on the inflammatory pathogenesis of CAD and suggest new options for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: Apoptosis; ITM2B; Inflammation; NK cell; T cell.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of Biomarkers Associated With CD8+ T Cells in Coronary Artery Disease and Their Pan-Cancer Analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 21;13:876616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.876616. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35799780 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarkers associated with phagocytosis regulatory factors in coronary artery disease using machine learning and network analysis.Mamm Genome. 2025 Jun;36(2):601-613. doi: 10.1007/s00335-025-10111-5. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Mamm Genome. 2025. PMID: 39953122 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying semaphorin 3C as a biomarker for sarcopenia and coronary artery disease via bioinformatics and machine learning.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2025 Apr;131:105762. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2025.105762. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 39827515
-
Elucidating the role of KCTD10 in coronary atherosclerosis: Harnessing bioinformatics and machine learning to advance understanding.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 10;15(1):8168. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91376-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40059128 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of key immune-related gene in Parkinson's disease based on WGCNA and machine learning.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Feb 28;49(2):207-219. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230307. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38755717 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Tsao, C. W. et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2023 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation147, e93–e621. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Everett, B. M. et al. Anti-Inflammatory therapy with Canakinumab for the prevention of hospitalization for heart failure. Circulation139, 1289–1299. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038010 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

