Dual role of miR-155 and exosomal miR-155 in tumor angiogenesis: implications for cancer progression and therapy
- PMID: 40383762
- PMCID: PMC12087080
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-02618-z
Dual role of miR-155 and exosomal miR-155 in tumor angiogenesis: implications for cancer progression and therapy
Abstract
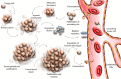
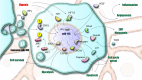
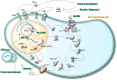
Tumor angiogenesis facilitates cancer progression by supporting tumor growth and metastasis. MicroRNA-155 (miR-155) plays a pivotal role in regulating angiogenesis through both direct effects on tumor and endothelial cells and indirect modulation via exosomal communication. This review highlights miR-155's pro-angiogenic influence on endothelial cell behavior and tumor microenvironment remodeling. Additionally, exosomal miR-155 enhances intercellular communication, promoting vascularization in several cancers. Emerging therapeutic strategies include miR-155 inhibition using antagomirs, exosome-mediated delivery systems, and modulation of pathways such as JAK2/STAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD2. Targeting miR-155 represents a promising approach to hinder tumor angiogenesis and improve cancer therapy outcomes.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cancer; Exosome; MicroRNA-155.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomal miR-320d promotes angiogenesis and colorectal cancer metastasis via targeting GNAI1 to affect the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Dec 18;15(12):913. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07297-y. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39695099 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma cell-secreted exosomal miR-155-5p induce proangiogenic switch of cancer-associated fibroblasts via SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 3;37(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0911-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30285793 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-derived exosomal miR-221-3p promotes angiogenesis by targeting THBS2 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Angiogenesis. 2019 Aug;22(3):397-410. doi: 10.1007/s10456-019-09665-1. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Angiogenesis. 2019. Retraction in: Angiogenesis. 2023 Feb;26(1):201. doi: 10.1007/s10456-022-09864-3. PMID: 30993566 Retracted.
-
Exosomal lncRNAs in the Tumor Angiogenesis: As Therapeutic Targets in Cancer Treatment.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025 Apr;358(4):e202400940. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202400940. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025. PMID: 40165644 Review.
-
Critical roles of miR-21 in promotions angiogenesis: friend or foe?Clin Exp Med. 2025 Feb 25;25(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01600-7. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39998742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-derived exosomes and their application in cancer treatment.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 8;23(1):751. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06814-7. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40629355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between innate-like T-cells and microRNAs in cancer immunity.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 28;16(1):1425. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03234-3. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40720066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giovannetti E, Erozenci A, Smit J, Danesi R, Peters GJ. Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in anticancer drug resistance and implications for clinical practice. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012;81(2):103–22. - PubMed
-
- Winter J, Diederichs S. MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;676:3–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

