Beyond the brain: exploring the impact of animal models of leptomeningeal disease from solid tumors
- PMID: 40383789
- PMCID: PMC12087207
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-025-01959-4
Beyond the brain: exploring the impact of animal models of leptomeningeal disease from solid tumors
Abstract
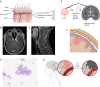
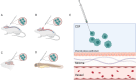
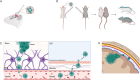
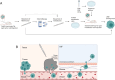
Leptomeningeal disease (LMD) is a devastating manifestation of late-stage cancer which currently suffers from a lack of effective therapeutics. Unfortunately, a significant obstacle preventing the widespread development and testing of therapeutics for LMD is the lack of biologically accurate animal models. We provide overviews of six types of animal models of leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors: injection of tumor cells into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood, or brain parenchyma; subcutaneous or mammary fat pad injection of tumor cells; the LeptoM/LM-phenotype model; and genetic manipulation. We identify the pros and cons of each model and suggest broad areas of future research that could improve each model in terms of its similarity to human LMD.
Keywords: Animal model; CSF; Cerebrospinal fluid; LMD; Leptomeningeal disease; Leptomeningeal metastasis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: JRT and AUA declare no competing interests. PK declares: Consulting Fee (e.g., Advisory Board): Enclear Therapies, Affinia Therapeutics, Biocept, Janssen, Bioclinica, Novocure, Mirati, Servier, Roche, Telix Pharmaceuticals, PlusTherapeutics, Belay Diagnostics, Biodexa Data Safety Monitoring Community: BPGBio, In8bio Speaker's Bureau: Seagen Contracted Research: Genentech, Novocure, DNAtrix, Orbus Therapeutics, Servier, Plus Therapeutics Provisional Patent issued for the treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis with ANG1005 Patent Number: WO2016/205367.
Figures


References
-
- Adile AA, Bakhshinyan D, Suk Y, Uehling D, Saini M, Aman A, Magolan J, Subapanditha MK, McKenna D, Chokshi C et al (2023) An effective kinase inhibition strategy for metastatic recurrent childhood medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 163:635–645. 10.1007/s11060-023-04372-w - PubMed
-
- Ahn JH, Lee SH, Kim S, Joo J, Yoo H, Lee SH, Shin SH, Gwak HS (2012) Risk for leptomeningeal seeding after resection for brain metastases: implication of tumor location with mode of resection. J Neurosurg 116:984–993. 10.3171/2012.1.JNS111560 - PubMed
-
- Alder L, Trapani D, Bradbury C, Van Swearingen AED, Tolaney SM, Khasraw M, Anders CK, Lascola CD, Hsu L, Lin NU et al (2023) Durable responses in patients with HER2+ breast cancer and leptomeningeal metastases treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan. NPJ Breast Cancer 9:19. 10.1038/s41523-023-00519-0 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alterman AL, Stackpole CW (1989) B16 melanoma spontaneous brain metastasis: occurrence and development within leptomeninges blood vessels. Clin Exp Metastasis 7:15–23. 10.1007/BF02057178 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

