Improved Machine Learning Predictions of EC50s Using Uncertainty Estimation from Dose-Response Data
- PMID: 40384077
- PMCID: PMC12152940
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00249
Improved Machine Learning Predictions of EC50s Using Uncertainty Estimation from Dose-Response Data
Abstract
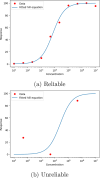
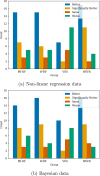
In early-stage drug design, machine learning models often rely on compressed representations of data, where raw experimental results are distilled into a single metric per molecule through curve fitting. This process discards valuable information about the quality of the curve fit. In this study, we incorporated a fit-quality metric into machine learning models to capture the reliability of metrics for individual molecules. Using 40 data sets from PubChem (public) and BASF (private), we demonstrated that including this quality metric can significantly improve predictive performance without additional experiments. Four methods were tested: random forests with parametric bootstrap, weighted random forests, variable output smearing random forests, and weighted support vector regression. When using fit-quality metrics, at least one of these methods led to a statistically significant improvement on 31 of the 40 data sets. In the best case, these methods led to a 22% reduction in the root-mean-squared error of the models. Overall, our results demonstrate that by adapting data processing to account for curve fit quality, we can improve predictive performance across a range of different data sets.
Figures




References
-
- Gomes M. N., Braga R. C., Grzelak E. M., Neves B. J., Muratov E., Ma R., Klein L. L., Cho S., Oliveira G. R., Franzblau S. G.. et al. QSAR-driven design, synthesis and discovery of potent chalcone derivatives with antitubercular activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017;137:126–138. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.05.026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

