Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Lamivudine-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles: In Vitro Cytotoxicity, Tissue Deposition, Biochemical Impact In Vivo, and Molecular Simulations Analysis
- PMID: 40384113
- PMCID: PMC12175167
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00182
Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Lamivudine-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles: In Vitro Cytotoxicity, Tissue Deposition, Biochemical Impact In Vivo, and Molecular Simulations Analysis
Abstract
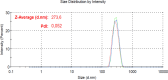
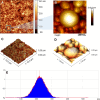
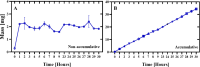
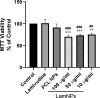
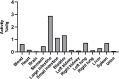
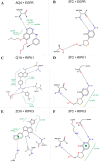
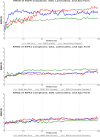
Lamivudine is a synthetic nucleoside analogue to cytosine with a modified sugar moiety. It has potent action against Human Immunodeficiency Virus and chronic hepatitis. Recently, studies have also shown that lamivudine (3TC) can induce apoptosis in cancer cells and inhibit their proliferation, including breast cancer. We prepared polymeric nanoparticles using the double emulsification technique to incorporate polycaprolactone (PCL) as the polymer and lamivudine as the active compound. The nanoparticles were characterized by atomic force microscopy and dynamic light scattering. Then we carried out a full set of in vitro and in vivo analyses, including measurement of cytotoxicity, radiolabeling, biodistribution and biochemistry. The results showed the formation of 273 nm spherical nanoparticles with monodisperse behavior (PDI = 0.052). The radiolabeling with 99mTc demonstrated the feasibility of the direct radiolabeling process. The cytotoxicity corroborated the potential against the triple-negative breast cancer line (MDA-MB-231). The biodistribution assay revealed high uptake in the liver, small and large intestines and bladder, besides the presence of nanoparticles in the urine. The in vivo biochemistry analysis showed alterations in some enzyme levels, including: alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma GT (GGT), creatinine (CRE), amylase (MAS), lactate dehydrogenase pyruvate (LDH-P) and glucose (GLU). Finally, we performed theoretical studies of molecular docking, molecular dynamics and interactions between lamivudine and key proteins regulating necroptosis, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), and receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3). Theoretical results showed lamivudine's adaptability to the binding sites of these proteins, with potential for optimization to enhance hydrophobic interactions and binding affinity. The findings demonstrated the efficacy of lamivudine against breast cancer cells, and the need to better understand the interplay of nanosystems with biochemical parameters.
Keywords: nanotechnology; oncology; radiolabeling; therapy; treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surface Charge Overrides Protein Corona Formation in Determining the Cytotoxicity, Cellular Uptake, and Biodistribution of Silver Nanoparticles.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jun 16;8(6):5032-5043. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00392. Epub 2025 May 21. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 40397405 Free PMC article.
-
Morin-Loaded Nanoalloy-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanoplatforms for Synergetic Chemotherapy to Target Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jul 21;8(7):5699-5717. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00382. Epub 2025 Jul 2. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 40601917
-
Synthesis of S-alkylated oxadiazole bearing imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole derivatives targeting breast cancer: In vitro cytotoxic evaluation and in vivo radioactive tracing studies.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Dec;153:107935. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107935. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39504637
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetics, and Drug Interaction Profile of Doravirine.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Dec;58(12):1553-1565. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00806-9. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 31388941 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
