Forging a New Frontier: Antimicrobial Peptides and Nanotechnology Converging to Conquer Gastrointestinal Pathogens
- PMID: 40384187
- PMCID: PMC12232244
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202501431
Forging a New Frontier: Antimicrobial Peptides and Nanotechnology Converging to Conquer Gastrointestinal Pathogens
Abstract
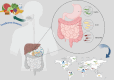
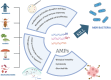
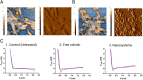
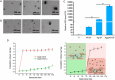
Gastrointestinal infections, which are caused primarily by pathogenic bacteria, remain a significant global health challenge. Their resilience is reinforced by various physical, biological, and biopharmaceutical barriers that complicate conventional therapeutic strategies. This review delves into the intricate landscape of managing these infections, addressing microbiota imbalances, the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains, and the impact of dysbiosis and antibiotic overuse. Faced with these challenges, traditional therapies often fail, which is hindered by low bioavailability, prolonged regimens, and a growing risk of resistance. In this context, nanotechnology applied to antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) has emerged as a promising solution to enhance their stability and targeted delivery. Through a critical approach, diverse nanocarriers and their efficacy against intestinal pathogens are evaluated both in vitro and in vivo. This review advocates for intensified research on the encapsulation and functionalization of AMPs, envisioning their potential to redefine the control of intestinal infections on a global scale.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptide; gastrointestinal infections; multidrug resistance; nanocarriers; nanoparticles.
© 2025 The Author(s). Small published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jiang Z., Li M., McClements D. J., Liu X., Liu F., Food Hydrocoll 2022, 125, 107438.
-
- Rogler G., Biedermann L., Scharl M., Swiss Med. Wkly. 2018, 148, w14599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

