Compact Origins and Where to Find Them: ORC's Guide to Genome-Wide Licensing
- PMID: 40384310
- PMCID: PMC12183775
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.70018
Compact Origins and Where to Find Them: ORC's Guide to Genome-Wide Licensing
Abstract
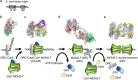
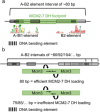
Origin licensing is the first step in the fundamental process of DNA replication, which ensures the accurate transmission of an organism's genetic information. Studies in budding yeast have provided crucial insights into replication origins, revealing sequence-specific features and structural DNA elements guiding helicase loading. Here, we review the recent advances in our understanding of DNA replication origin licensing, focusing on insights into origin architecture and advancements in high-resolution sequencing. Progress in the field demonstrates that origins are compact units that load an individual MCM2-7 double hexamer, which in turn causes steric occlusion of the origin recognition complex (ORC) binding site. We discuss why, in addition to the DNA sequence, DNA shape, DNA flexibility, and correct spacing of A- and B2-elements are crucial for efficient helicase loading. These recent findings provide a mechanistic explanation for the regulation of genome-wide origin licensing and reveal fundamental principles of MCM2-7 helicase loading.
Keywords: ChIP‐Exo; DNA licensing; DNA replication; MCM2‐7; ORC; budding yeast; origins.
© 2025 The Author(s). BioEssays published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MCM2-7 loading-dependent ORC release ensures genome-wide origin licensing.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 24;15(1):7306. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51538-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39181881 Free PMC article.
-
An Orc6 tether mediates ORC binding site switching during replication origin licensing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 13:2025.05.09.652650. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.09.652650. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40462942 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Replication origin-flanking roadblocks reveal origin-licensing dynamics and altered sequence dependence.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21417-21430. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.815639. Epub 2017 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29074622 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for licensing origins of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Jul;32(7):1143-1153. doi: 10.1038/s41594-025-01587-5. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40588663 Review.
-
How similar are the molecular mechanisms of yeast and metazoan genome replication initiation?Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Mar 7;53(2):353-61. doi: 10.1042/BST20220917. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40052964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

