Shen Shuai II Recipe alleviates renal fibrosis in chronic kidney disease by improving of hypoxia and inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- PMID: 40384385
- PMCID: PMC12090266
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2502875
Shen Shuai II Recipe alleviates renal fibrosis in chronic kidney disease by improving of hypoxia and inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
Abstract
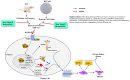
Objectives: To investigate the anti-fibrotic mechanisms of Shen Shuai II Recipe (SSR) in chronic kidney disease (CKD), focusing on its modulation of hypoxia-associated inflammatory pathways and the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB/NLRP3 axis.
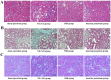
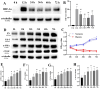
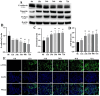
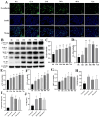
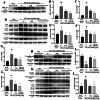
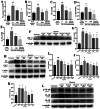
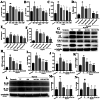
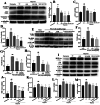
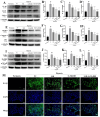
Methods: A 5/6 nephrectomy-induced chronic renal failure (CRF) rat model and hypoxia-exposed human renal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells were utilized. In vivo, renal function was assessed via serum creatinine, urea nitrogen, and creatinine clearance measurements, alongside histopathological evaluation of renal fibrosis and inflammation. In vitro, hypoxia-treated HK-2 cells were analyzed for fibrotic markers (fibronectin, collagen I, α-smooth muscle actin) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-18). Molecular mechanisms were probed through protein expression analysis of HIF-1α and the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway, with NLRP3 inflammasome activity evaluated.
Results: SSR treatment significantly improved renal function in CRF rats, reducing serum creatinine (Scr) and urea nitrogen (BUN) while enhancing creatinine clearance. Histopathology revealed preserved renal architecture with attenuated fibrosis and inflammatory infiltration. In hypoxic HK-2 cells, SSR downregulated fibrotic markers and suppressed IL-1β and IL-18 levels. Mechanistically, SSR reduced HIF-1α expression, inhibited TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling, and suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation in both models.
Conclusions: SSR alleviates renal fibrosis and CKD progression by mitigating hypoxia-driven inflammation and blocking the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway.
Keywords: Shen Shuai II Recipe (SSR); TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB; hypoxia; inflammation; renal interstitial fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Huangkui capsule alleviates renal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and TLR4/NF-κB signaling.Phytomedicine. 2019 Apr;57:203-214. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.021. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30785016
-
Shen-Shuai-II-Recipe inhibits tubular inflammation by PPARα-mediated fatty acid oxidation to attenuate fibroblast activation in fibrotic kidneys.Phytomedicine. 2024 Apr;126:155450. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155450. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38368794
-
Effects of the TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway on NLRP3 Inflammasome in Coronary Microembolization-Induced Myocardial Injury.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(4):1497-1508. doi: 10.1159/000490866. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29940584
-
Flavonoids in Combating Renal Fibrosis: Targeting NF-κB Signal and In Silico Support.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Jun;22(6):e202403022. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202403022. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39924970 Review.
-
Heart failure, inflammation and exercise.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Apr 28;21(8):3324-3350. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.109917. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520009 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
