GRB2 Promotes Malignant Behaviors of Breast Cancer by Modulating the Global Expression and Alternative Splicing Profiles in SK-BR-3 Cells Through Binding mRNA
- PMID: 40384436
- PMCID: PMC12086363
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70905
GRB2 Promotes Malignant Behaviors of Breast Cancer by Modulating the Global Expression and Alternative Splicing Profiles in SK-BR-3 Cells Through Binding mRNA
Abstract
Purpose: The flexible protein GRB2 interacts with HER1-4 on the cell surface and regulates the development of tumor cells; meanwhile, it is also an RBP that plays an important role in post-transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes, which affects every stage of mRNA synthesis, modification, splicing, and stabilization. Although some studies have found a connection between GRB2 and HER2-overexpression breast cancer, highlighting the potential of GRB2 as a novel biomarker that stimulates tumor growth, limited data were available to elaborate on their interaction mechanisms.
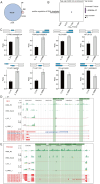
Methods: In this research, we found 396 different gene expressions between the Grb2-knockdown group and the SK-BR-3 group by the RNA sequencing approach. After GRB2 was knocked down, 956 alternative splicing events occurred.
Results: The fRIP-seq results showed that GRB2-binding reads were significantly enriched in the intron region, indicating that UUAGC and UUGGUUGG might be the binding motifs. An integration analysis of DEGs with the peak genes of fRIP-seq revealed that 63 genes possess GRB2 binding sites on their mRNAs or antisense RNAs. By integration analysis of AS events with the peak genes of fRIP-seq, 66 genes related to AS events were found.
Conclusions: Above, these AS events may be regulated by GRB2 to promote the progression of HER2-overexpression breast cancer.
Keywords: GRB2; RBPs; alternative splicing; breast cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GRB2 promotes brain metastasis in HER2-positive breast cancer by regulating the Ras/MAPK pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 27;15(1):14736. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99685-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40289214 Free PMC article.
-
miR-411-5p inhibits proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cell via targeting GRB2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Aug 5;476(4):607-613. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.006. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27264952
-
The adaptor proteins p66Shc and Grb2 regulate the activation of the GTPases ARF1 and ARF6 in invasive breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):5687-703. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.516047. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24407288 Free PMC article.
-
KHSRP has oncogenic functions and regulates the expression and alternative splicing of DNA repair genes in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 26;14(1):14694. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64687-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38926398 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Grb2 in Cancer and Peptides as Grb2 Antagonists.Protein Pept Lett. 2018 Feb 8;24(12):1084-1095. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666171123213148. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 29173143 Review.
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., et al., “Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 71, no. 3 (2021): 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Wagle N. S., and Jemal A., “Cancer Statistics, 2023,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 73, no. 1 (2023): 17–48. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D., “Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions,” Cancer Discovery 12, no. 1 (2022): 31–46. - PubMed
-
- Tao X., Li T., Gandomkar Z., Brennan P. C., and Reed W. M., “Incidence, Mortality, Survival, and Disease Burden of Breast Cancer in China Compared to Other Developed Countries,” Asia‐Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology 19, no. 6 (2023): 645–654. - PubMed
-
- Burrell R. A., McGranahan N., Bartek J., and Swanton C., “The Causes and Consequences of Genetic Heterogeneity in Cancer Evolution,” Nature 501, no. 7467 (2013): 338–345. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021D01C411/Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
- 2022TCYCLHY/Tianchi Talents-Young Doctor Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
- TSYC202301B094/Tianshan Talents-High-level medical and health personnel training program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
- 2023TSLJ0038/Tianshan Talents-Leading Talents in Science and Technology Innovation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

