Molecular characterization of a synthetic neutralizing antibody targeting p67 of Theileria parva
- PMID: 40384600
- PMCID: PMC12086512
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.70153
Molecular characterization of a synthetic neutralizing antibody targeting p67 of Theileria parva
Abstract
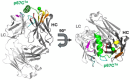
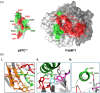
The Theileria parva sporozoite surface antigen p67 is a target of the bovine humoral immune response that generates antibodies capable of providing protection against subsequent infection. As a result, p67 has been the subject of efforts aimed at the development of an anti-sporozoite subunit vaccine. Previous studies have identified neutralizing epitopes in the N- and C-terminal regions of the full-length protein and shown that immunization with a C-terminal fragment of p67 (p67C) alone is capable of eliciting protection. To identify additional neutralizing epitopes in p67C, selections were conducted against it using a phage-displayed synthetic antibody library. An antibody that neutralized the sporozoite in vitro was identified, and the crystal structure of a Fab:peptide complex was elucidated. Mutagenesis studies aimed at validating and further characterizing the Fab:peptide interaction identified critical residues involved in binding and neutralization. This study also validates distinct epitopes for previously reported neutralizing antibodies.
Keywords: Theileria parva; crystal structure; neutralizing; p67; parasite; synthetic antibody.
© 2025 The Author(s). Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures

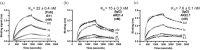
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse‐Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002;58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Anon . The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett S, Eichenberger RM, Nevagi RJ, Ghaffar KA, Marasini N, Dai Y, et al. Lipopeptide‐based Oral vaccine against hookworm infection. J Infect Dis. 2020;221:934–942. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

