Automatic segmentation of calibration device boundaries on ophthalmic optical biometry instruments in optical coherence tomography images
- PMID: 40384692
- PMCID: PMC12084751
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-2051
Automatic segmentation of calibration device boundaries on ophthalmic optical biometry instruments in optical coherence tomography images
Abstract
Background: As the use of ophthalmic optical biometers in clinical practice has increased, so too has the demand for higher standards in evaluating ocular metrics. Among these metrics, the measurement of the ocular axial length (AL) is a critical task that often requires calibrated devices. Thus, efficient algorithms need to be developed to improve calibration mechanisms and ensure precise measurements. This study aimed to establish an algorithm to determine the pixel heights (PHs) of the boundary vertices of a calibration device in ophthalmic optical biometers to improve the accuracy and repeatability of ocular AL measurements in optical coherence tomography (OCT) images.
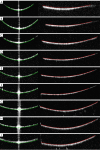
Methods: The algorithm employs a series of image morphological processing techniques to delineate the rough boundaries of the calibration device in OCT images. After extracting boundary points, clustering techniques are applied to simplify the data. These clustered boundary points are analyzed for characteristic parameters to refine the boundaries. Finally, a fitting process is used to determine the PHs of the vertices, and performance is then evaluated by tests measuring the repeatability and recognition accuracy of the algorithm.
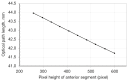
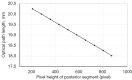
Results: The proposed method had high repeatability in locating the boundaries of the front and rear sections of the calibration device, and had repeatability deviations not exceeding 0.36 pixels and 0.18 pixels, respectively. Additionally, linear fitting of the computed sub-PH and optical path difference yielded determination coefficients of 0.9998330 and 0.9999863, respectively, indicating an almost perfectly linear relationship. This high degree of linearity demonstrates the exceptional accuracy of the method in locating the calibration device boundaries. These results provide a heuristic approach for the future boundary localization of calibration devices in OCT images for biometers, offering a robust and reliable framework for enhancing calibration precision in ophthalmic optical biometry.
Conclusions: The developed algorithm provides an effective and reliable method for determining the PHs of calibration device vertices in ophthalmic optical biometers. With its high accuracy and repeatability, this valuable tool could enhance ocular AL measurements and improve the overall quality of ocular assessments in clinical practice.
Keywords: Optical coherence tomography (OCT); anterior segment; image segmentation; optical biometer calibration devices; posterior segment.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-2051/coif). F.C. is an employee of Suzhou Big Vision Medical Imaging Technology Co., Ltd.; however, no conflicts of interest arose in relation to the content of this article and his affiliation. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Lee CY, Jeng YT, Yang SF, Huang CT, Chao CC, Lian IB, Huang JY, Chang CK. Topographic and Surgical Risk Factors for Early Myopic Regression between Small Incision Lenticule Extraction and Laser In Situ Keratomileusis. Diagnostics (Basel) 2024;14:1275. 10.3390/diagnostics14121275 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
