Predicting cardiac resynchronization therapy response: development and validation of a single photon emission computed tomography-based nomogram
- PMID: 40384719
- PMCID: PMC12084738
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-2024-2700
Predicting cardiac resynchronization therapy response: development and validation of a single photon emission computed tomography-based nomogram
Abstract
Background: Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is an effective treatment for patients with drug-refractory heart failure. However, more than thirty percent of patients do not benefit from CRT. This study aimed to develop and validate a novel model based on single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) phase analysis features to predict CRT response.
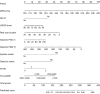
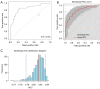
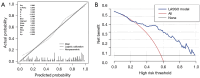
Methods: We identified 163 CRT patients who received gated resting SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) between 2010 and 2020 at The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. All variables were first processed by univariate logistic regression, and those with a P value <0.05 were retained. The selected variables were subsequently used in the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression to construct a predictive model, which was then represented as a nomogram. Nomogram performance was assessed via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration curves, and decision curve analyses (DCAs). Internal validation was performed by bootstrapping with 1,000 replicates.
Results: Of the 163 patients, 93 (57.1%) responded to CRT during follow-up. Responders had a wider QRS complex duration (QRSd) (164.80 vs. 154.51 ms, P=0.003), fewer premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) (1,392.98 vs. 2,283.60, P=0.003), lower prevalence of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (NS-VT) (45.2% vs. 77.1%, P<0.001), and better cardiac function [based on N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), New York Heart Association (NYHA), and left ventricle (LV) parameters] compared to non-responders. Univariate logistic regression revealed 14 variables significantly associated with CRT response (all P<0.05). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) value for the nomogram was 0.845 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.785-0.906; sensitivity: 0.771; specificity: 0.849]. Internal validation yielded a mean AUC of 0.814 (95% CI: 0.777-0.836). The calibration curve demonstrated strong consistency between the predicted and observed outcomes. DCA revealed that the nomogram consistently provides a net benefit over the baseline, demonstrating its high practical value in clinical decision-making. A web-based dynamic nomogram (https://jzw20000624.shinyapps.io/CRTpredictionmodel/) was developed for clinical application.
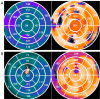
Conclusions: We developed and validated a SPECT-based prediction model for predicting CRT response, which can assist clinicians in optimizing CRT candidacy preoperatively. Pacing at the latest contraction and relaxation segments, while avoiding scarred regions and optimizing preoperative status, is anticipated to improve CRT response.
Keywords: Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); nomogram; phase analysis technique; single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-2024-2700/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Texture Analysis of SPECT-MPI Provides Prognostic Value in Improving Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Response.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2025 Jun;48(6):630-639. doi: 10.1111/pace.15200. Epub 2025 May 20. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2025. PMID: 40391672
-
Effective prediction of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy using a novel program of gated myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography.Europace. 2011 Dec;13(12):1731-7. doi: 10.1093/europace/eur143. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Europace. 2011. PMID: 21873328
-
A nomogram for predicting CRT response based on multi-parameter features.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04033-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39030503 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative gated SPECT-derived phase analysis on gated myocardial perfusion SPECT detects left ventricular dyssynchrony and predicts response to cardiac resynchronization therapy.J Nucl Med. 2009 May;50(5):718-25. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.060657. J Nucl Med. 2009. PMID: 19403876 Clinical Trial.
-
A novel method combining gated SPECT and vectorcardiography to guide left ventricular lead placement to improve response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: A proof of concept study.J Nucl Cardiol. 2024 Jun;36:101867. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclcard.2024.101867. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Nucl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38697386
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
