Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy: A Focus on Advances in Diagnosis and Management
- PMID: 40384732
- PMCID: PMC12082475
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcvj.1580
Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy: A Focus on Advances in Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
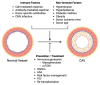
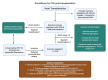
Cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) is a type of coronary artery disease unique to heart transplant recipients that can result from chronic rejection of the transplanted heart. CAV is a major cause of morbidity and mortality after the first year of transplantation. Both immune and nonimmune mechanisms contribute to the initiation and progression of CAV and result in intimal thickening, fibrosis with luminal stenosis, chronic myocardial ischemia and eventual graft failure. Recent advances in imaging modalities-including invasive intracoronary imaging and noninvasive imaging with cardiac positron emission tomography-have improved the early detection of CAV and may allow for optimization of CAV-targeted therapies to reduce CAV progression and ultimately preserve graft function.
Keywords: IVUS; PET; coronary angiography; heart transplant; mTORi; rejection; vasculopathy.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Khush KK, Cherikh WS, Chambers DC, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult heart transplantation report - 2019; focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019. Oct;38(10):1056-66. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Day JD, Rayburn BK, Gaudin PB, et al. Cardiac allograft vasculopathy: the central pathogenetic role of ischemia-induced endothelial cell injury. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1995. Nov-Dec;14(6 Pt 2):S142-9. PMID: 8719476 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

