Mathematical modeling and estimation of physicochemical characteristics of pneumonia treatment drugs through a novel approach K-Banhatti topological descriptors
- PMID: 40384760
- PMCID: PMC12081363
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1564809
Mathematical modeling and estimation of physicochemical characteristics of pneumonia treatment drugs through a novel approach K-Banhatti topological descriptors
Abstract
Introduction: Pneumonia is the primary cause of mortality in preterm infants in developing nations; yet, early detection and treatment can significantly reduce mortality rates. Pharmaceutical researchers are diligently striving to identify avariety of drugs that might effectively cure pneumonia.
Method: We are motivated to examine the quantitative structureproperty relationships (QSPR) of anti-pneumonia pharmaceuticals. We employed K-Banhatti topological descriptors and analyzed the findings to achieve this. For estimation of physicochemical properties of pneumonia treatment drugs we utilized linear, quadratic, cubic, and biquadratic regression analyses.
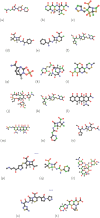
Results and conclusion: The drugs comprise linezolid, ceftabiprole, and clarithromycin, among others. Topological descriptors enable the exploration of the complexity, connectivity, and other essential attributes of molecules. The quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) analysis of pharmaceuticals for illness treatment employing K-Banhatti topological descriptors is an economical approach utilised by pharmaceutical researchers. We performed a QSPR analysis on 20 anti-pneumonia drugs to ascertain the most precise predictions for five properties: enthalpy, flash point, molecular weight, molar volume, and molar refractivity, employing five K-Banhatti indices. To do this, we used linear, quadratic, cubic, and biquadratic regression analyses to find links between molecules and the physical and chemical properties of drugs used to treat pneumonia. Employing molecular descriptors and regression models to investigate chemical patterns is a cost-effective and theoretical methodology.
Keywords: K-Banhatti descriptors; QSPR testing; anti-pneumonia drugs; chemical graph theory; molecular structure; physicochemical properties; regression models; topological descriptors.
Copyright © 2025 Khan, Naeem, Tchier, Tolasa and Hussain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chemical graphs, molecular matrices and topological indices in chemoinformatics and quantitative structure-activity relationships.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2013 Jun;9(2):153-63. doi: 10.2174/1573409911309020002. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2013. PMID: 23701000 Review.
-
Chemical applicability and computation of K-Banhatti indices for benzenoid hydrocarbons and triazine-based covalent organic frameworks.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 18;13(1):17743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45061-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37853135 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Neighborhood Topological Descriptors for Quantitative Structure-property Relationship (QSPR) Analysis and Entropy Measures of Some Anti-cancer Drugs.Curr Org Synth. 2025 Feb 10. doi: 10.2174/0115701794349166241217085334. Online ahead of print. Curr Org Synth. 2025. PMID: 39950293
-
Eccentric indices based QSPR evaluation of drugs for schizophrenia treatment.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 23;11(2):e42222. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42222. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39925359 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative approaches in QSPR modelling using topological indices for the development of cancer treatments.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 21;20(2):e0317507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317507. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39982891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almalki N., Tabassum H. (2024). On K-banhatti, revan indices and entropy measures of MgO (111) nanosheets via linear regression. Mathematics 12 (4), 561. 10.3390/math12040561 - DOI
-
- Anjum M. S., Safdar M. U. (2019). K Banhatti and K hyper-Banhatti indices of nanotubes. Eng. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2(1), 19–37. 10.30538/psrp-easl2019.0013 - DOI
-
- Awan N. U. H., Ghaffar A., Tawfiq F. M., Mustafa G., Bilal M. (2024). QSPR analysis for physiochemical properties of new potential antimalarial compounds involving topological indices. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 124 (11), e27391. 10.1002/qua.27391 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

