Concordance of DLQI and pain score in hidradenitis suppurativa clinical trials: a systematic review
- PMID: 40384776
- PMCID: PMC12080693
- DOI: 10.1097/JW9.0000000000000204
Concordance of DLQI and pain score in hidradenitis suppurativa clinical trials: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, recurrent inflammatory condition and is associated with significant psychosocial impacts on patient quality of life.
Objective: This study aimed to characterize the utilization of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in HS clinical trials and their concordance with trial primary endpoints.
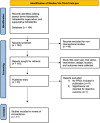
Methods: A systematic review of clinical trials was performed using the publicly available U.S. National Library of Medicine (ClinicalTrials.gov) in June 2023 utilizing the search terms hidradenitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and suppurativa hidradenitis. Study title, start year, trial status, intervention, design, location, and primary and secondary outcomes were collected. To assess for concordance of patient and provider-reported outcomes, we identified published placebo-controlled trials that included Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and/or a numeric rating scale (NRS) for pain, the 2 most utilized PROs.
Results: One hundred sixty-four HS clinical trials were identified, of which 115 were interventional studies. A total of 65.2% (n = 107) of HS trials included at least one PRO. Pain NRS (42.7%, n = 70) and DLQI (42.1%, n = 69) were the most frequently used PRO instruments. The use of PROs in clinical trials increased over time, with 50% of trials between 2020 and 2023 utilizing PROs. Of 11 published HS trials, 82% (n = 9) trials showed concordance of provider-assessed and PROs in at least one treatment arm.
Limitations: Significance and standard deviations of PROs were rarely reported, preventing the calculation of significance and is a limitation of this review.
Conclusion: While lesion counts provide single snapshots of disease, PROs can capture perceptions of lesions not actively present. PROs are frequently concordant with both achievement and nonachievement of primary endpoints in clinical trials.
Keywords: DLQI; HiSCR; biologics; hidradenitis suppurativa; pain; patient-reported outcomes.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of Women’s Dermatologic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors made the following disclosures: A.R.M. has no relevant disclosures. He has consulted for Kyowa, Eli Lilly, Momenta, UCB, and Regeneron in the past, greater than 24 months ago. He has consulted for PHELEC in the past, great than 12 months. He has consulted for Incyte, Soligenix, Clarivate, and Bristol Myers Squibb in the past, less than 12 months ago. He consults for Argenyx, Boehringer, Janssen, and Ingelheim currently. He consults for Regeneron and Pfizer currently with payments to the institution. He has grant support from Kyowa, Miragen, Regeneron, Corbus, Pfizer, Incyte, Eli Lilly, Aregenx, Palbella, Abbvie, Priovant, Merck in the last 24 months. Beyond 24 months, grant support has come from Sun Pharma, Elorac, Novartis, and Janssen. His current patents include Methods and Materials for assessing and treating cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (provisional 63-423254), use of oral JAKi in Lichen Planus (provisional 63/453,065), and Topical Ruxolitinib in Lichen Planus (WO2022072814A1). The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Gnanasakthy A, Barrett A, Evans E, D’Alessio D, Romano CD. A review of patient-reported outcomes labeling for oncology drugs approved by the FDA and the EMA (2012-2016). Value Health 2019;22:203–9. - PubMed
-
- Ingram JR. The epidemiology of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol 2020;183:990–8. - PubMed
-
- Basra MK, Salek MS, Camilleri L, Sturkey R, Finlay AY. Determining the minimal clinically important difference and responsiveness of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): further data. Dermatology 2015;230:27–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
