De-succinylation-induced accumulation of TRMT10C in the nucleus plays a detrimental role in coronary microembolization via its m1A modification function
- PMID: 40384859
- PMCID: PMC12080399
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.107965
De-succinylation-induced accumulation of TRMT10C in the nucleus plays a detrimental role in coronary microembolization via its m1A modification function
Abstract
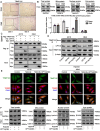
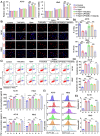
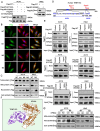
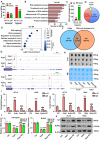
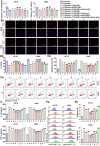
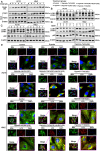
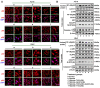
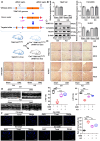
Coronary microembolization (CME) refers to embolism in the coronary microcirculation. This study showed a reduction in succinyl transferase (CPT1A) and the succinylation substrate (succinyl-CoA) in cardiomyocytes in CME models, suppressing the succinylation of the mitochondrially localized protein TRMT10C. Suppression of succinylation promotes KPNA4 recognition of two nuclear localization signals (NLSs), KAKR and KKK(X)10KVKK, in TRMT10C, which induces the transport of TRMT10C from the cytoplasm to the nucleus rather than to the mitochondria. Nuclear TRMT10C induces YTHDF2-mediated decay of TAFAZZIN and NLRX1 through m1A modifications. The reduction in TAFAZZIN and NLRX1 is associated with multiple detrimental effects, such as inflammation mediated by NF-κB and NLRP3, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and suppression of mitophagy. TRMT10C knockdown suppressed the accumulation of TRMT10C in the nucleus. It restored NLRX1 and TAFAZZIN protein levels in cardiomyocytes under hypoxia. However, the deficiency of TRMT10C in the mitochondria did not improve-or even worsened-with TRMT10C knockdown. Inducing TRMT10C succinylation via CPT1A overexpression led to the redistribution of TRMT10C to the mitochondria rather than the nucleus, which is likely a better approach for improving cardiomyocyte function under hypoxia than direct TRMT10C knockdown. This study reveals a novel pathological mechanism underlying CME and suggests potential therapeutic targets for this disease.
Keywords: TRMT10C; coronary microembolization; inflammation; m1A modification; mitophagy; nuclear localization; succinylation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

