Neferine Ameliorates Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Intestinal Injury by Promoting NRF2-mediated Ferroptosis
- PMID: 40384872
- PMCID: PMC12080392
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.112888
Neferine Ameliorates Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Intestinal Injury by Promoting NRF2-mediated Ferroptosis
Abstract
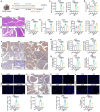
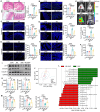
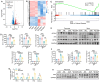
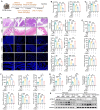
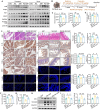
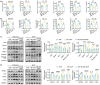
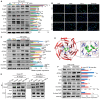
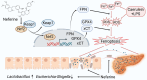
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is a life-threatening abdominal condition often complicated by intestinal barrier dysfunction, which further exacerbates disease progression. Neferine has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties; however, its role in ameliorating SAP and associated intestinal barrier damage remains unclear. In this study, we found that neferine administration significantly alleviates SAP severity by reducing pancreatic and ileal pathological damage, oxidative stress, inflammatory cell infiltration, and intestinal flora translocation. Additionally, neferine enhances the expression of tight junction proteins, increases short-chain fatty acid levels, and improves intestinal dysbiosis, thereby contributing to intestinal homeostasis restoration. Mechanistically, neferine upregulates Nrf2 expression and promotes its nuclear translocation by competitively binding to the Cys-288 site on Keap1. This activation enhances the Nrf2/FPN and Nrf2/xCT/GPX4 axes, thereby preventing ferroptosis and ultimately protecting against pancreatic and intestinal injury in SAP mice. Furthermore, the protective effects of neferine were largely reversed by the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 and the ferroptosis inducer erastin. This study demonstrates that neferine effectively alleviates SAP by inhibiting ferroptosis and restoring intestinal homeostasis, providing insights into new treatment options for SAP.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Ferroptosis; Gut microbiota; Intestinal injury; Iron export; Neferine.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Chaitoff A, Cifu AS, Niforatos JD. Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Jama. 2020;323:2331–2. - PubMed
-
- Sendler M, van den Brandt C, Glaubitz J, Wilden A, Golchert J, Weiss FU. et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulates Development of Systemic Inflammatory Response and Compensatory Anti-Inflammatory Response Syndromes in Mice With Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:253–69.e14. - PubMed
-
- Beger HG, Rau B, Mayer J, Pralle U. Natural course of acute pancreatitis. World J Surg. 1997;21:130–5. - PubMed
-
- Cui QR, Ling YH, Wen SH, Liu KX, Xiang YK, Yang WJ. et al. Gut Barrier Dysfunction Induced by Aggressive Fluid Resuscitation in Severe Acute Pancreatitis is Alleviated by Necroptosis Inhibition in Rats. Shock. 2019;52:e107–e16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

