Microtubule dynamics is a therapeutic vulnerability in VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40384876
- PMCID: PMC12080383
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.109642
Microtubule dynamics is a therapeutic vulnerability in VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
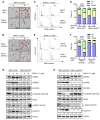
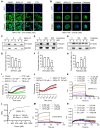
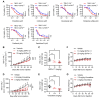
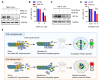
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) is a tumor suppressor frequently mutated in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and its loss has been considered as a target for therapeutic exploitation. In an effort to identify therapeutic vulnerabilities in VHL-deficient RCC, we found that SKPin C1, a SKP2 inhibitor, exhibited synthetic lethal effects on VHL-deficient RCC cells. SKPin C1 selectively disrupted spindle assembly in VHL-deficient RCC, leading to the induction of mitotic arrest and death. These effects were independent of its inhibitory action on SKP2. Our in-depth biochemical and molecular interaction studies reveal that SKPin C1 binds to tubulin and inhibits microtubule polymerization. Interestingly, anti-microtubule effect of SKPin C1 was much more pronounced in VHL-deficient RCC cells. Further mechanistic studies on the synthetic lethality reveal that VHL loss alters microtubule dynamics in cells, promoting microtubule growth speed while reducing stability. Treatment of VHL-deficient RCC cells with SKPin C1 or other microtubule destabilizers strongly suppressed microtubule growth and reduced the levels of GTP-tubulin and acetylated microtubules, resulting in selective vulnerability in VHL-deficient RCC. Taken together, our study suggests that microtubule dynamics is a therapeutic vulnerability in VHL-deficient RCC and provides a rationale for the combination treatment of VHL-deficient RCC with anti-microtubule agents and RCC targeted therapies.
Keywords: VHL; drug target; microtubule; renal cell carcinoma; synthetic lethality.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Kjaer M, Frederiksen PL, Engelholm SA. Postoperative radiotherapy in stage II and III renal adenocarcinoma. A randomized trial by the Copenhagen Renal Cancer Study Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1987;13:665–72. - PubMed
-
- Amato RJ. Chemotherapy for renal cell carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2000;27:177–86. - PubMed
-
- Gez E, Libes M, Bar-Deroma R, Rubinov R, Stein M, Kuten A. Postoperative irradiation in localized renal cell carcinoma: the Rambam Medical Center experience. Tumori. 2002;88:500–2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

