Exoskeletons for the rehabilitation of temporomandibular disorders: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40384880
- PMCID: PMC12081923
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2025.1492275
Exoskeletons for the rehabilitation of temporomandibular disorders: a comprehensive review
Abstract
Despite the many technological advancements in exoskeletons for the rehabilitation of lower or upper limbs, there has been limited exploration of their application in treating temporomandibular disorders, a set of musculoskeletal and neuromuscular conditions affecting the masticatory system. By collecting data, implementing assisting and resisting training routines, and encouraging active patient engagement, exoskeletons could provide controlled and individualized exercise with flexibility in time and location to aid in the recovery or improvement of jaw mobility and function. Thus, they might offer a valuable alternative or complement to conservative physiotherapy. In this context, the review aims to draw attention to rehabilitating temporomandibular disorders with the help of exoskeletons by looking at the advantages and opportunities these devices potentially provide. After stating the requirements and resulting scientific challenges in various fields and discussing the state of the art, existing research gaps and deficiencies will be discussed, highlighting areas where further research and development is needed.
Keywords: TMD; exoskeletons; physical therapy; rehabilitation; review; robotics; temporomandibular disorders.
Copyright © 2025 Müller, Sader and von Stryk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

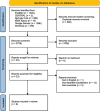



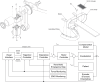



References
-
- Agarwal P., Deshpande A. D. (2019). “234Exoskeletons: state-of-the-art, design challenges, and future directions,” in Human performance optimization: the science and ethics of enhancing human capabilities (Oxford University Press; ). 10.1093/oso/9780190455132.003.0011 - DOI
-
- Ariji Y., Katsumata A., Ogi N., Izumi M., Sakuma S., Iida Y., et al. (2009). An oral rehabilitation robot for massaging the masseter and temporal muscles: a preliminary report. Oral Radiol. 25, 53–59. 10.1007/s11282-009-0014-0 - DOI
-
- Ariji Y., Nakayama M., Nishiyama W., Ogi N., Sakuma S., Katsumata A., et al. (2015). Potential clinical application of masseter and temporal muscle massage treatment using an oral rehabilitation robot in temporomandibular disorder patients with myofascial pain. CRANIO® 33, 256–262. 10.1179/2151090314y.0000000030 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

